Is Fungi Autotrophic Or Heterotrophic? Unraveling The Mystery Of Fungal Nutrition
Are you curious about whether fungi are autotrophic or heterotrophic? This question often arises when studying the fascinating world of fungi and their role in ecosystems. Fungi, a diverse group of organisms, play a crucial role in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and symbiotic relationships. Unlike plants, fungi do not photosynthesize, which immediately sets them apart in terms of how they obtain energy. So, is fungi autotrophic or heterotrophic? Understanding this distinction is essential for appreciating their unique biology and ecological significance.
Fungi are classified as heterotrophs, meaning they cannot produce their own food through processes like photosynthesis. Instead, they rely on external sources of organic matter to meet their nutritional needs. This characteristic places them in stark contrast to autotrophic organisms like plants, which use sunlight to create energy. By exploring the mechanisms fungi use to acquire nutrients, we can better understand their role in maintaining ecological balance and their impact on human life.
From decomposing organic material to forming symbiotic partnerships with plants, fungi exhibit remarkable adaptability. Their heterotrophic nature enables them to break down complex compounds and recycle nutrients back into the environment. In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the question, "Is fungi autotrophic or heterotrophic?" and uncover the intricate ways fungi contribute to the natural world. Let’s begin by examining the fundamental differences between autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Read also:Who Was Amy Winehouses Last Partner And What Made Their Relationship So Intriguing
- Understanding Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
- Is Fungi Autotrophic or Heterotrophic?
- How Do Fungi Obtain Nutrients?
- Why Are Fungi Considered Heterotrophs?
- The Role of Fungi in Ecosystems
- Can Fungi Ever Be Autotrophic?
- Fungal Symbiosis with Plants
- Decomposers of the Natural World
- Common Misconceptions About Fungi
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs?
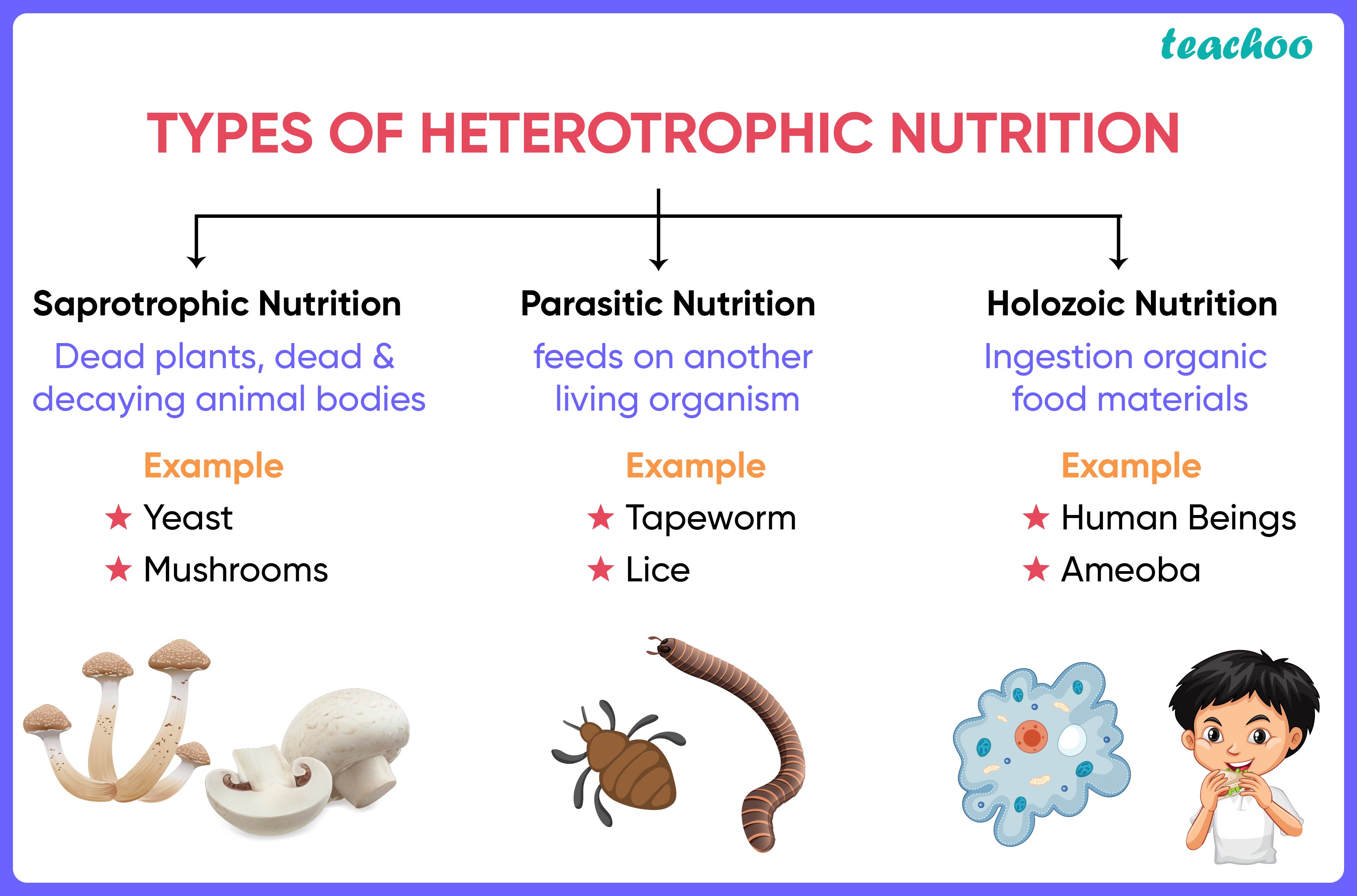
To answer the question, "Is fungi autotrophic or heterotrophic?" we must first understand the basic definitions of these terms. Autotrophs are organisms that produce their own food using energy from sunlight (photosynthesis) or chemical reactions (chemosynthesis). Plants, algae, and some bacteria are examples of autotrophs. On the other hand, heterotrophs are organisms that cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms or organic matter to survive. Animals, fungi, and many bacteria fall into this category.
The distinction between autotrophs and heterotrophs is fundamental in biology. Autotrophs form the base of the food chain, providing energy and nutrients to other organisms. Heterotrophs, including fungi, rely on these autotrophs or other heterotrophs to meet their nutritional requirements. This dependency shapes their ecological roles and interactions with the environment.
Is Fungi Autotrophic or Heterotrophic?
Fungi are heterotrophic organisms, meaning they cannot produce their own food. Unlike plants, fungi lack chlorophyll, the pigment necessary for photosynthesis. Instead, they obtain nutrients by breaking down organic matter in their surroundings. This characteristic places fungi firmly in the heterotrophic category. But what exactly does this mean for their survival and ecological function?
How Do Fungi Obtain Nutrients?
Fungi employ a variety of strategies to obtain nutrients. They secrete enzymes that break down complex organic compounds into simpler molecules, which they can then absorb. This process is known as external digestion. Fungi can decompose dead plants, animals, and other organic materials, making them essential recyclers in ecosystems.
Why Are Fungi Considered Heterotrophs?
The inability of fungi to produce their own food is the primary reason they are classified as heterotrophs. Their reliance on external organic matter distinguishes them from autotrophic organisms. This dependency also explains their diverse roles in ecosystems, from decomposers to symbiotic partners.
What Role Do Fungi Play in Ecosystems?
Fungi are indispensable in maintaining ecological balance. They break down dead organic matter, returning essential nutrients to the soil. This decomposition process supports plant growth and sustains the food web. Additionally, fungi form symbiotic relationships with plants, such as mycorrhizal associations, which enhance nutrient uptake for both partners.
Read also:Exploring The Life And Achievements Of Aneesha Joshi
Can Fungi Ever Be Autotrophic?
While fungi are predominantly heterotrophic, some species exhibit unique adaptations that blur the line between autotrophy and heterotrophy. For example, certain fungi form associations with photosynthetic organisms, indirectly benefiting from the energy produced through photosynthesis. However, these fungi are still classified as heterotrophs since they do not produce their own food directly.
How Do Fungi Form Symbiotic Relationships with Plants?
Fungi engage in mutualistic relationships with plants, particularly through mycorrhizal associations. In these partnerships, fungi provide plants with increased access to water and nutrients, while plants supply fungi with carbohydrates. This symbiosis highlights the versatility and adaptability of fungi in their ecological roles.
Why Are Fungi Called Decomposers of the Natural World?
Fungi are often referred to as nature’s recyclers because they break down dead organisms and organic waste. This decomposition process releases nutrients back into the environment, supporting new growth and maintaining ecosystem health. Without fungi, the accumulation of organic matter would disrupt nutrient cycles.
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Fungi?
One common misconception is that fungi are plants. While they share some similarities, fungi are a distinct kingdom with unique characteristics. Another misconception is that all fungi are harmful. In reality, many fungi are beneficial, playing vital roles in ecosystems and human industries such as medicine and agriculture.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are All Fungi Heterotrophic?
Yes, all fungi are heterotrophic. They rely on external organic matter for nutrition and cannot produce their own food through processes like photosynthesis.
How Do Fungi Contribute to Human Life?
Fungi contribute to human life in numerous ways, from providing food (e.g., mushrooms) to producing antibiotics (e.g., penicillin). They also play a role in biotechnology and environmental sustainability.
What Would Happen Without Fungi in Ecosystems?
Without fungi, ecosystems would suffer from the accumulation of dead organic matter, disrupting nutrient cycles and threatening the survival of plants and animals.
In conclusion, fungi are heterotrophic organisms that play a vital role in ecosystems and human life. Understanding whether fungi are autotrophic or heterotrophic helps us appreciate their unique biology and ecological significance. By breaking down organic matter and forming symbiotic relationships, fungi contribute to the health and balance of the natural world.
Skald Reviews: Unveiling The Truth About Side Effects
How Much Does It Cost To Live In Hawaii? A Complete Guide To Budgeting In Paradise
Unlock The Power Of Vanilla: Your Ultimate Guide To Vanillagify.com

SOLUTION What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and
Heterotrophic Nutrition Definition, Types, Examples Teachoo