Is Fungi Heterotrophic Or Autotrophic? Uncovering The Truth About Fungi's Nutrition
Fungi, a diverse group of organisms, play a crucial role in decomposition, nutrient cycling, and even food production. However, their method of obtaining nutrients has sparked curiosity among scientists and enthusiasts alike. This article dives deep into the question: **Is fungi heterotrophic or autotrophic?** By exploring their biological mechanisms, ecological roles, and unique characteristics, we aim to provide a comprehensive answer.
Fungi differ significantly from plants and animals in how they acquire energy and nutrients. While plants are autotrophic, producing their own food through photosynthesis, fungi rely on external sources for sustenance. This dependency raises the question of whether fungi can be classified as heterotrophic organisms. To fully understand this, we must examine their cellular structure, metabolic processes, and interactions with other organisms. By doing so, we can uncover the fascinating ways fungi sustain themselves and contribute to the environment.
The answer to whether fungi are heterotrophic or autotrophic lies in their unique biological adaptations. Fungi lack chlorophyll, the pigment essential for photosynthesis, which eliminates the possibility of them being autotrophic. Instead, they obtain nutrients by breaking down organic matter, forming symbiotic relationships, or acting as parasites. This adaptability has allowed fungi to thrive in diverse environments, from dense forests to human-made structures. Let’s explore the intricacies of fungi’s nutritional strategies in detail.
Read also:Everything You Need To Know About Matilda Djerf Age And Her Inspiring Journey
Table of Contents
- What Are Fungi?
- Is Fungi Heterotrophic or Autotrophic?
- How Do Fungi Obtain Nutrients?
- Why Are Fungi Classified as Heterotrophs?
- Can Fungi Be Autotrophic?
- Types of Heterotrophic Fungi
- What Roles Do Fungi Play in Ecosystems?
- How Do Fungi Interact With Other Organisms?
- Are There Any Exceptions to Fungi Being Heterotrophic?
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Fungi?
Fungi are a kingdom of organisms that include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. They are neither plants nor animals, occupying a unique position in the biological classification system. Fungi are eukaryotic, meaning their cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Unlike plants, they lack chlorophyll and cannot perform photosynthesis. This absence of photosynthetic ability is a key factor in determining whether fungi are heterotrophic or autotrophic.
Is Fungi Heterotrophic or Autotrophic?
The question **is fungi heterotrophic or autotrophic** can be answered by examining their mode of nutrition. Fungi are heterotrophic, meaning they obtain their nutrients from external sources rather than producing them internally. They achieve this through various methods, such as decomposing organic matter, forming mutualistic relationships, or acting as parasites. This heterotrophic nature sets them apart from autotrophic organisms like plants.
How Do Fungi Obtain Nutrients?
Fungi use specialized structures called hyphae to absorb nutrients from their surroundings. These thread-like structures secrete enzymes that break down complex organic compounds into simpler molecules, which the fungi then absorb. This process is known as external digestion. For example, saprophytic fungi decompose dead plant and animal matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Why Are Fungi Classified as Heterotrophs?
Fungi are classified as heterotrophs because they cannot produce their own food. Unlike autotrophic organisms, they lack the ability to convert sunlight or inorganic materials into energy. Instead, they rely on organic matter for sustenance. This dependency on external sources is a defining characteristic of heterotrophic organisms, including fungi.
Can Fungi Be Autotrophic?
Given their biological makeup, fungi cannot be autotrophic. They lack chlorophyll and other essential components required for photosynthesis. However, some fungi form symbiotic relationships with autotrophic organisms, such as algae in lichens. In these partnerships, the fungi benefit from the sugars produced by their photosynthetic partners, but this does not make them autotrophic.
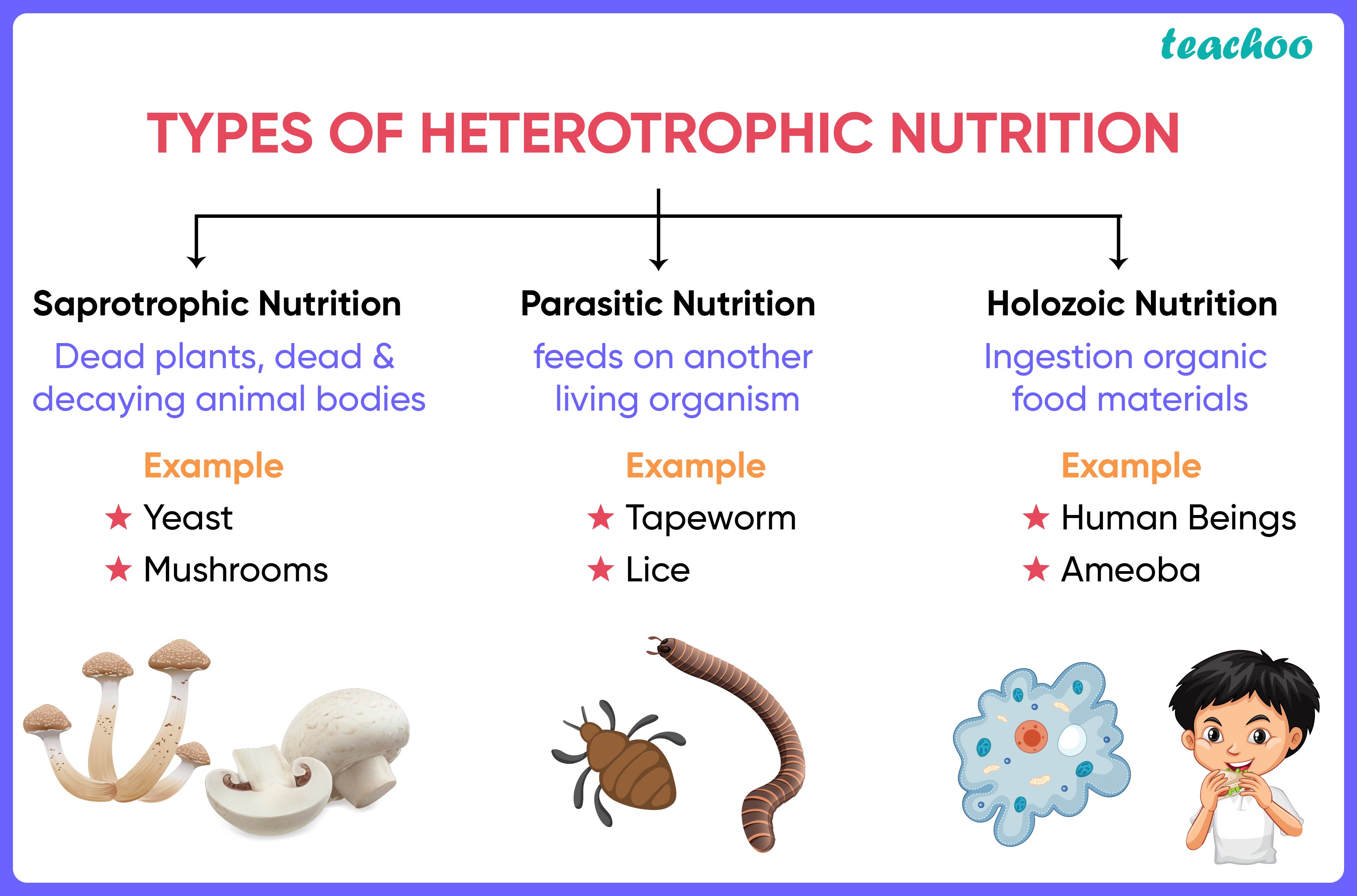
Types of Heterotrophic Fungi
Heterotrophic fungi can be categorized into three main types based on their nutritional strategies:
Read also:Discovering Sean Gunn The Versatile Talent Behind The Camera And On Screen
- Saprophytic Fungi: These fungi decompose dead organic matter, playing a vital role in nutrient recycling.
- Parasitic Fungi: These fungi derive nutrients from living hosts, often causing diseases in plants and animals.
- Mutualistic Fungi: These fungi form beneficial relationships with other organisms, such as mycorrhizal fungi that assist plants in nutrient absorption.
What Roles Do Fungi Play in Ecosystems?
Fungi are indispensable to ecosystems due to their ability to break down organic matter and recycle nutrients. They act as nature’s recyclers, decomposing dead plants and animals and returning essential elements like carbon and nitrogen to the soil. Additionally, fungi form symbiotic relationships with plants, enhancing their ability to absorb water and minerals.
How Do Fungi Interact With Other Organisms?
Fungi interact with other organisms in various ways, including mutualism, parasitism, and commensalism. For example, mycorrhizal fungi form mutualistic relationships with plant roots, exchanging nutrients for carbohydrates. In contrast, parasitic fungi harm their hosts by extracting nutrients, often leading to diseases like athlete’s foot or ringworm.
Are There Any Exceptions to Fungi Being Heterotrophic?
While fungi are predominantly heterotrophic, some exceptions exist. For instance, certain fungi in lichens benefit from the photosynthetic activity of their algal partners. However, these fungi still rely on external sources for energy, maintaining their heterotrophic classification. The question **is fungi heterotrophic or autotrophic** remains firmly answered in favor of heterotrophy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does Heterotrophic Mean?
Heterotrophic organisms obtain their nutrients from external sources rather than producing them internally. This contrasts with autotrophic organisms, which can generate their own food through processes like photosynthesis.
Why Can’t Fungi Perform Photosynthesis?
Fungi lack chlorophyll, the pigment necessary for photosynthesis. Without this pigment, they cannot convert sunlight into energy, making them reliant on organic matter for sustenance.
Do All Fungi Decompose Organic Matter?
No, not all fungi decompose organic matter. While saprophytic fungi specialize in decomposition, other types, such as parasitic and mutualistic fungi, obtain nutrients through different means.
How Do Fungi Benefit Humans?
Fungi benefit humans in numerous ways, from producing antibiotics like penicillin to serving as food sources like mushrooms. They also play a critical role in agriculture by enhancing soil fertility through decomposition and symbiotic relationships.
In conclusion, the question **is fungi heterotrophic or autotrophic** highlights the unique biological characteristics of fungi. Their heterotrophic nature enables them to play vital roles in ecosystems, interact with other organisms, and contribute to human life. By understanding their nutritional strategies and ecological significance, we can appreciate the complexity and importance of fungi in the natural world.
How Old Is Luffy: Unveiling The Age Of The Pirate King In The Making
Lake Or Pond: Discovering The Beauty And Differences
How Expensive Is Hawaii To Live: A Complete Guide To Costs And Lifestyle

SOLUTION What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and
Heterotrophic Nutrition Definition, Types, Examples Teachoo