Understanding 6 Gauge Wire Amps: A Complete Guide
When it comes to electrical wiring, understanding the capabilities of different wire gauges is essential for safety and efficiency. The 6 gauge wire amps rating is a critical factor for anyone working on electrical projects, whether you're wiring a home, installing an appliance, or setting up a workshop. This guide will explore everything you need to know about 6 gauge wire amps, from its capacity to its applications and safety considerations. With the increasing demand for reliable electrical systems, knowing how to choose the right wire gauge can make all the difference in ensuring your project runs smoothly and safely.
Choosing the correct wire gauge is not just about meeting code requirements; it’s about protecting your property and ensuring optimal performance. A 6 gauge wire is commonly used in applications requiring higher current loads, such as large appliances, HVAC systems, and even electric vehicle charging stations. Understanding its ampacity—the maximum current it can safely carry—is crucial to avoid overheating, electrical fires, or system failures. This article will break down the technical details and practical uses of 6 gauge wire amps so you can make informed decisions.
Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or a professional electrician, knowing the ins and outs of 6 gauge wire amps can save you time, money, and potential hazards. We’ll also cover common mistakes to avoid and tips for selecting the right wire for your needs. By the end of this guide, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of 6 gauge wire amps and how they fit into your electrical projects, ensuring both safety and efficiency.
Read also:Exploring The Legacy Of James Caans Son A Rising Star In Hollywood
Table of Contents
- What is 6 Gauge Wire Amps?
- How Many Amps Can a 6 Gauge Wire Handle?
- Why Choose 6 Gauge Wire for High-Amp Applications?
- Is 6 Gauge Wire Amps Suitable for Your Project?
- Common Mistakes When Using 6 Gauge Wire Amps
- How to Calculate Ampacity for 6 Gauge Wire?
- Applications of 6 Gauge Wire Amps
- How Does Temperature Affect 6 Gauge Wire Amps?
- Safety Tips for Using 6 Gauge Wire Amps
- Frequently Asked Questions About 6 Gauge Wire Amps
What is 6 Gauge Wire Amps?
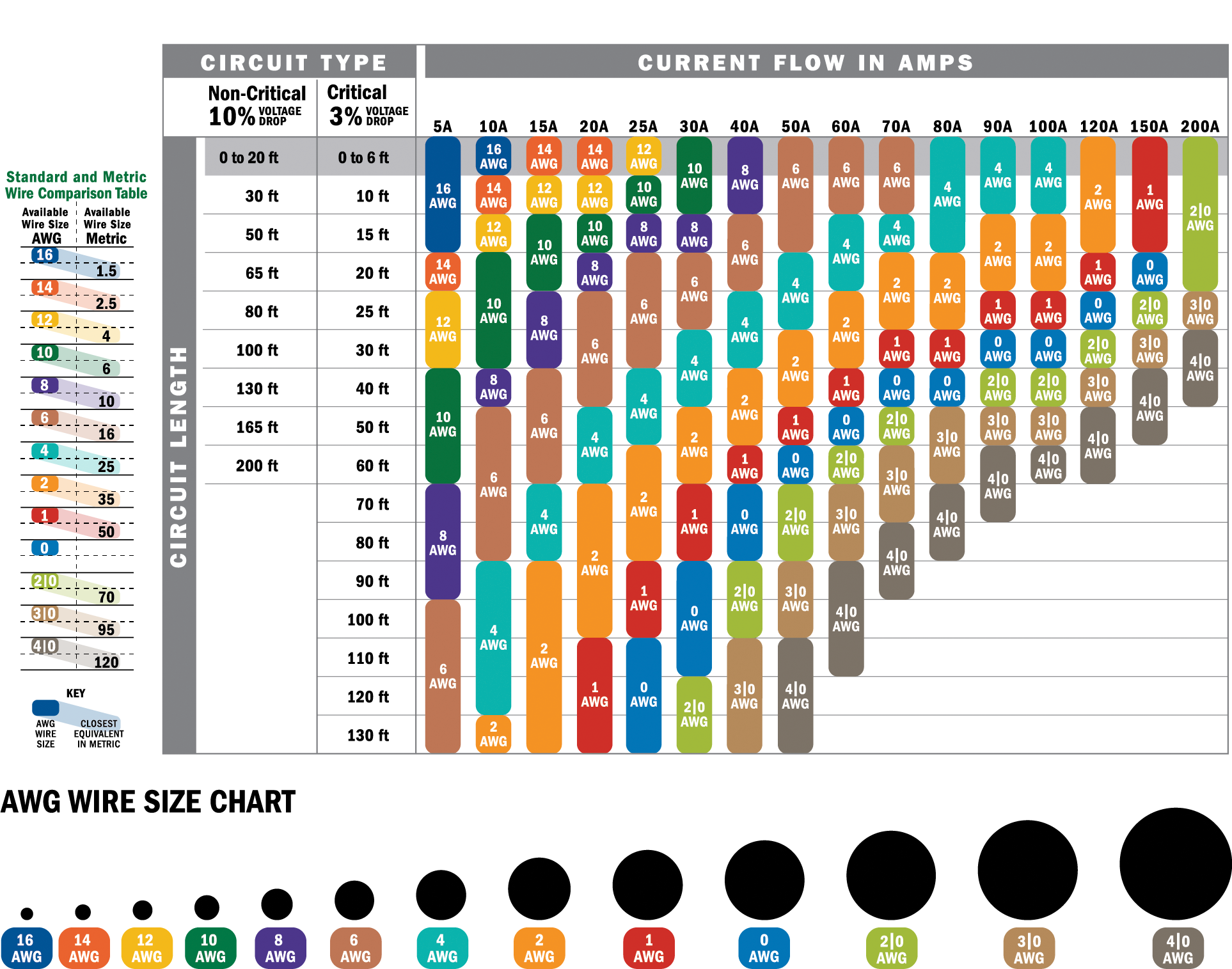
6 gauge wire amps refer to the maximum current capacity that a 6 AWG (American Wire Gauge) wire can safely carry without overheating. This rating is determined by factors such as the wire's material (copper or aluminum), insulation type, and environmental conditions. For copper wires, the general ampacity of a 6 gauge wire is around 55 amps at 75°C, while aluminum wires typically handle around 40 amps under the same conditions.
Understanding the ampacity of a wire is crucial for ensuring that your electrical system operates safely and efficiently. Exceeding the rated ampacity of a wire can lead to overheating, which may cause insulation damage, electrical fires, or equipment failure. Always consult the National Electrical Code (NEC) or a certified electrician to confirm the appropriate wire gauge for your specific application.
How Many Amps Can a 6 Gauge Wire Handle?
One of the most common questions about 6 gauge wire amps is how much current it can safely handle. As mentioned earlier, a 6 gauge copper wire can typically carry up to 55 amps, while an aluminum wire of the same gauge can handle around 40 amps. These ratings are based on standard conditions, such as ambient temperature and proper installation practices.
However, it's important to note that these numbers can vary depending on factors like the type of insulation, the length of the wire, and the temperature of the environment. For example, wires installed in hot environments may have reduced ampacity due to increased resistance. Always check the manufacturer's specifications and adhere to local electrical codes to ensure safe operation.
Why Choose 6 Gauge Wire for High-Amp Applications?
6 gauge wire amps make it an excellent choice for applications requiring high current loads. Its thicker diameter reduces resistance, allowing it to carry more current without overheating. This makes it ideal for powering large appliances, such as electric stoves, water heaters, and air conditioning units.
Additionally, 6 gauge wire amps are often used in industrial settings, workshops, and even electric vehicle charging stations. Its durability and ability to handle heavy loads make it a reliable option for projects where safety and performance are paramount. By choosing the right wire gauge, you can ensure that your electrical system operates efficiently and remains safe for years to come.
Read also:Discovering Zoe Perry And Her Father A Journey Into Family Talent And Legacy
Is 6 Gauge Wire Amps Suitable for Your Project?
Before purchasing 6 gauge wire amps, it's essential to evaluate whether it's the right choice for your specific project. Factors such as the length of the wire run, the type of load, and the environment in which the wire will be installed all play a role in determining suitability. For example, if you're wiring a long-distance circuit, you may need to upgrade to a thicker gauge to compensate for voltage drop.
To determine if 6 gauge wire amps are suitable, consider the following:
- What is the maximum current your circuit will carry?
- What is the length of the wire run?
- What are the environmental conditions (temperature, moisture, etc.)?
Consulting an electrician or using an online ampacity calculator can help you make an informed decision.
Common Mistakes When Using 6 Gauge Wire Amps
Even experienced electricians can make mistakes when working with 6 gauge wire amps. One common error is underestimating the importance of proper insulation. Using a wire with inadequate insulation for high-temperature environments can lead to overheating and potential hazards.
Another mistake is failing to account for voltage drop over long distances. Using a wire that's too thin for the length of the circuit can result in reduced performance and increased energy consumption. To avoid these issues, always follow the manufacturer's guidelines and adhere to local electrical codes.
How to Calculate Ampacity for 6 Gauge Wire?
Calculating the ampacity of 6 gauge wire amps involves considering several factors, including the wire's material, insulation type, and environmental conditions. For a quick estimate, you can refer to the NEC's ampacity tables, which provide standardized ratings for different wire gauges and materials.
To calculate ampacity manually, use the following formula:
- Determine the wire's resistance per unit length.
- Calculate the voltage drop based on the wire's length and current load.
- Adjust for environmental factors such as temperature and insulation type.
For accurate results, consider using an online calculator or consulting a professional electrician.
Applications of 6 Gauge Wire Amps
6 gauge wire amps are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications. Some common uses include:
- Powering large appliances such as electric stoves and water heaters.
- Wiring HVAC systems and air conditioning units.
- Installing electric vehicle charging stations.
- Setting up workshops and industrial equipment.
Its ability to handle high current loads makes it a reliable choice for projects where safety and performance are critical.
How Does Temperature Affect 6 Gauge Wire Amps?
Temperature plays a significant role in determining the ampacity of 6 gauge wire amps. Higher temperatures increase the wire's resistance, which can reduce its current-carrying capacity. For example, a wire rated for 55 amps at 75°C may only handle 45 amps at 90°C.
To account for temperature variations, always check the manufacturer's specifications and ensure that the wire is installed in an environment that matches its rated conditions. If you're working in a hot environment, consider upgrading to a thicker gauge or using wire with higher temperature-rated insulation.
Safety Tips for Using 6 Gauge Wire Amps
Using 6 gauge wire amps safely requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Always follow the manufacturer's guidelines and local electrical codes.
- Ensure proper insulation for the environment in which the wire will be installed.
- Use a circuit breaker that matches the wire's ampacity to prevent overloading.
- Inspect the wire regularly for signs of wear or damage.
By adhering to these safety practices, you can minimize the risk of electrical hazards and ensure the longevity of your wiring system.
Frequently Asked Questions About 6 Gauge Wire Amps
What is the maximum length for 6 gauge wire amps? The maximum length depends on the current load and voltage drop. For most residential applications, a 6 gauge wire can safely run up to 50 feet without significant voltage drop.
Can I use 6 gauge wire for a 50-amp circuit? Yes, a 6 gauge copper wire is suitable for a 50-amp circuit, provided it meets the necessary conditions for insulation and temperature.
What is the difference between copper and aluminum 6 gauge wire amps? Copper wires generally have higher ampacity and better conductivity than aluminum wires, making them more suitable for high-current applications.
Russia Legal Age Of Consent: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover The Magic Of Vanillagift.come: Your Ultimate Guide To Unique Gifts
Pond Vs Lake: Understanding The Key Differences And Similarities
20 Gauge Wire Amps

What Gauge Wire To Use For 240v 20 Amps