Understanding The Right 100 Amp Wire Gauge For Your Electrical Needs
Choosing the correct wire gauge for a 100 amp service is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency in your electrical system. Whether you're upgrading your home's electrical panel or installing a subpanel in your workshop, knowing the appropriate wire size can prevent overheating, voltage drops, and potential fire hazards. A 100 amp wire gauge is designed to handle the specific current load without compromising performance. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about selecting the right wire gauge for a 100 amp circuit and why it matters for your electrical projects.
Electrical systems are the backbone of modern homes and businesses, and using the wrong wire size can lead to costly repairs and dangerous situations. A 100 amp wire gauge is commonly used for residential and small commercial applications, but understanding its specifications and limitations is essential. Factors such as the distance of the wire run, the material of the wire (copper or aluminum), and the ambient temperature can all influence the wire size you need. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of how to make the best choice for your electrical setup.
Many people overlook the importance of wire gauge when planning electrical installations, but it plays a critical role in system performance. A 100 amp wire gauge ensures that the circuit can handle the required current without excessive resistance, which could lead to energy loss or overheating. This article will provide detailed insights into the technical aspects of wire gauges, practical tips for installation, and answers to common questions about 100 amp wire gauge. Let’s dive into the details to help you make informed decisions for your electrical needs.
Read also:Discovering Ulie Graham A Comprehensive Guide To His Life And Achievements
Table of Contents
- What is a 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
- How Do You Choose the Right Wire Gauge for 100 Amps?
- Why Does Wire Material Matter for 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
- What Are the Common Mistakes with 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
- Can You Use Aluminum Wire for 100 Amp Service?
- How Does Distance Affect 100 Amp Wire Gauge Selection?
- What Are the Safety Tips for Using 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
- How to Install a 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
- Why Is Proper Insulation Important for 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
- How to Troubleshoot Issues with 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
What is a 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
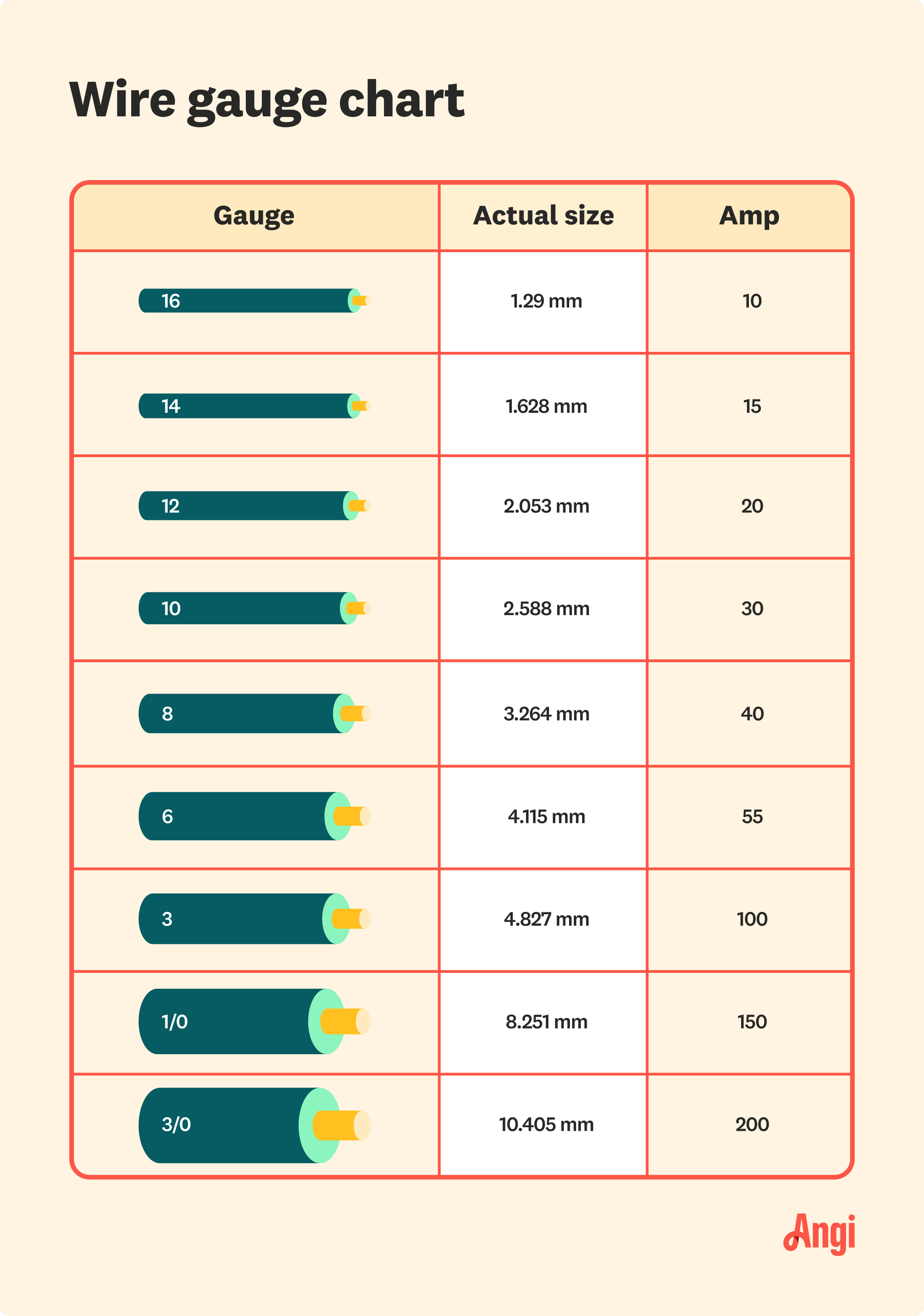
A 100 amp wire gauge refers to the thickness of the wire used to carry 100 amps of electrical current safely. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is commonly used to measure wire thickness, with lower numbers indicating thicker wires. For a 100 amp service, the recommended wire gauge is typically 2 AWG for copper wires and 1/0 AWG for aluminum wires. These sizes are designed to handle the current load without overheating or causing voltage drops.
The wire gauge is determined by several factors, including the type of material, the length of the wire run, and the ambient temperature. Copper wires are more conductive than aluminum, which means they can carry the same current with a smaller gauge. However, aluminum wires are often used in larger installations due to their lower cost and lighter weight.
How Do You Choose the Right Wire Gauge for 100 Amps?
Choosing the correct wire gauge for a 100 amp service involves evaluating the specific requirements of your electrical system. Here are some key considerations:
- Wire Material: Copper is more conductive than aluminum, so it requires a smaller gauge for the same current load.
- Distance: Longer wire runs require thicker gauges to minimize voltage drops.
- Temperature: Higher ambient temperatures can reduce the wire's current-carrying capacity.
For most residential applications, a 2 AWG copper wire or 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is sufficient for a 100 amp service. However, if the wire run exceeds 100 feet, you may need to upgrade to a thicker gauge to ensure optimal performance.
Why Does Wire Material Matter for 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
The material of the wire plays a significant role in determining the appropriate gauge for a 100 amp service. Copper wires are preferred for their superior conductivity and resistance to corrosion. They can carry the same current as aluminum wires with a smaller gauge, making them ideal for shorter runs and tighter spaces.
Aluminum wires, on the other hand, are less expensive and lighter, making them a popular choice for larger installations. However, they require a larger gauge to compensate for their lower conductivity. For example, a 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is equivalent to a 2 AWG copper wire for a 100 amp service.
Read also:Czech Wife Swap Exploring A Unique Cultural Phenomenon
What Are the Common Mistakes with 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
When working with a 100 amp wire gauge, several common mistakes can compromise safety and performance. Understanding these pitfalls can help you avoid costly errors.
- Using the Wrong Gauge: Using a wire that is too thin for the current load can lead to overheating and fire hazards.
- Ignoring Distance: Longer wire runs require thicker gauges to prevent voltage drops.
- Improper Connections: Poorly made connections can increase resistance and cause overheating.
To avoid these mistakes, always consult the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines and work with a licensed electrician if you're unsure about your installation.
Can You Use Aluminum Wire for 100 Amp Service?
Yes, you can use aluminum wire for a 100 amp service, but there are important considerations to keep in mind. Aluminum wires are less conductive than copper, so they require a larger gauge to handle the same current load. For a 100 amp service, a 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is typically recommended.
Aluminum wires are also more prone to corrosion and require special connectors to ensure a secure and durable connection. If you choose aluminum wire, make sure to use connectors specifically designed for aluminum to prevent issues like overheating and arcing.
How Does Distance Affect 100 Amp Wire Gauge Selection?
The distance of the wire run is a critical factor when selecting a 100 amp wire gauge. Longer runs result in higher resistance, which can cause voltage drops and reduce the efficiency of your electrical system. To compensate for this, you may need to use a thicker gauge wire.
For example, if your wire run exceeds 100 feet, you might need to upgrade from a 2 AWG copper wire to a 1 AWG copper wire to maintain optimal performance. Always calculate the voltage drop based on the wire length and current load to ensure your system operates safely and efficiently.
What Are the Safety Tips for Using 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
Safety should always be your top priority when working with electrical systems. Here are some essential tips for using a 100 amp wire gauge safely:
- Follow NEC Guidelines: Always adhere to the National Electrical Code recommendations for wire size and installation.
- Use Proper Connectors: Ensure all connections are secure and use connectors designed for the wire material.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the wire's current-carrying capacity to prevent overheating.
Regularly inspect your electrical system for signs of wear or damage, and address any issues promptly to maintain safety and performance.
How to Install a 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
Installing a 100 amp wire gauge requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Plan the Wire Run: Measure the distance and determine the appropriate gauge based on the current load and material.
- Choose the Right Wire: Select a wire that meets the NEC guidelines for your specific application.
- Prepare the Connections: Use proper connectors and ensure all connections are tight and secure.
- Test the System: After installation, test the system to ensure it operates safely and efficiently.
If you're not experienced with electrical work, it's always best to hire a licensed electrician to handle the installation.
Why Is Proper Insulation Important for 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
Proper insulation is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of a 100 amp wire gauge. Insulation protects the wire from environmental factors like moisture, heat, and physical damage, which can compromise its performance. It also prevents electrical shorts and ensures the wire can handle the current load without overheating.
When selecting wire, choose one with insulation rated for the voltage and temperature conditions of your application. For example, THHN/THWN insulation is commonly used for indoor and outdoor applications due to its durability and resistance to moisture and heat.
How to Troubleshoot Issues with 100 Amp Wire Gauge?
If you encounter issues with your 100 amp wire gauge, it's important to identify and address the problem promptly. Here are some common troubleshooting steps:
- Check for Overheating: Look for signs of discoloration or melting around the wire or connections.
- Inspect Connections: Ensure all connections are tight and free of corrosion.
- Measure Voltage Drop: Use a multimeter to check for excessive voltage drops along the wire run.
If you're unable to resolve the issue, consult a licensed electrician to diagnose and fix the problem safely.
Exploring The Challenges Of Harnessing Wave Energy
Understanding The Calorie Content Of White Bread
Discover The Magic Of Vanila Gift.com: Your Ultimate Gifting Destination
What Is the Correct Wire Size for 100Amp Service? Angi

Speaker wire gauge calculator vetkiza