Understanding White Bread Nutrition: A Comprehensive Guide
White bread is one of the most commonly consumed bread types worldwide, known for its soft texture and mild flavor. However, its nutritional value has been a topic of debate among health-conscious individuals. While it is often criticized for being less nutritious compared to whole-grain alternatives, understanding the nuances of white bread nutrition can help you make informed dietary choices. This article dives into the key nutritional aspects of white bread, its health implications, and how it fits into a balanced diet.
White bread is made from refined wheat flour, which undergoes a process that removes the bran and germ, leaving behind the starchy endosperm. This refining process gives white bread its characteristic light texture but also strips away many essential nutrients. Despite this, white bread is often enriched with vitamins and minerals to compensate for the lost nutrients. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone looking to balance taste preferences with nutritional needs.
As you explore the world of white bread nutrition, you'll discover how it compares to other bread types, its role in different diets, and whether it can be part of a healthy eating plan. Whether you're a fitness enthusiast, a parent planning meals for your family, or someone simply curious about nutrition, this guide will provide valuable insights to help you make better food decisions.
Read also:Discovering The Journey Of Daniel Radcliffe Age Career And Legacy
Table of Contents
- What is White Bread Nutrition?
- Is White Bread Nutrition Beneficial for Health?
- How Does White Bread Nutrition Compare to Whole Grain?
- What Are the Key Nutrients in White Bread?
- Can White Bread Be Part of a Balanced Diet?
- What Are the Health Risks of White Bread?
- How to Choose Healthier White Bread Options?
- What Are Some Alternatives to White Bread?
- Why Is Fortification Important in White Bread Nutrition?
- What Experts Say About White Bread Nutrition?
What is White Bread Nutrition?
White bread nutrition refers to the vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients present in white bread. The primary ingredients include refined wheat flour, water, yeast, and salt. During the refining process, the bran and germ are removed, which results in a loss of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. However, many manufacturers enrich white bread by adding nutrients like iron, B vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and folic acid), and sometimes calcium.
Despite its reputation as a "less healthy" option, white bread can still provide energy through its carbohydrate content. A single slice of white bread typically contains around 70-80 calories, with most of these calories coming from carbohydrates. Protein and fat content are relatively low, making it a lighter option for those monitoring their macronutrient intake.
Understanding white bread nutrition is essential for individuals with specific dietary needs, such as those managing diabetes or seeking to maintain a balanced diet. While it may not be the most nutrient-dense bread option, it can still play a role in a well-rounded eating plan when consumed in moderation.
Is White Bread Nutrition Beneficial for Health?
Read also:Young Jason Statham The Early Years Of An Action Icon
Many people wonder whether white bread nutrition can offer any health benefits. The answer lies in how it is consumed and the overall dietary context. White bread is often fortified with essential nutrients, which can contribute to daily vitamin and mineral intake. For instance, folic acid, a B vitamin commonly added to white bread, is crucial for pregnant women to support fetal development.
However, white bread's low fiber content can be a downside for digestive health. Fiber is essential for maintaining a healthy gut and preventing constipation. Since white bread lacks the bran and germ, it contains significantly less fiber than whole-grain alternatives. This can lead to quicker digestion and a spike in blood sugar levels, which may not be ideal for individuals with insulin sensitivity issues.
That said, white bread can still be beneficial in certain scenarios. For example, athletes or individuals needing quick energy may find white bread a convenient source of carbohydrates. The key is to balance its consumption with other nutrient-rich foods to ensure a well-rounded diet.
How Does White Bread Nutrition Compare to Whole Grain?
When comparing white bread nutrition to whole-grain bread, the differences are significant. Whole-grain bread retains the bran, germ, and endosperm, making it richer in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. This higher fiber content supports better digestion, prolonged satiety, and more stable blood sugar levels.
On the other hand, white bread is often criticized for its lower nutritional density. While it may be enriched with certain vitamins and minerals, it still lacks the natural nutrients found in whole grains. For example, whole-grain bread typically contains more magnesium, zinc, and antioxidants, which are beneficial for overall health.
Despite these differences, white bread can still have a place in your diet if consumed mindfully. Pairing it with protein-rich foods like eggs or nut butter can help balance its nutritional profile. Ultimately, the choice between white bread and whole-grain bread depends on your dietary goals and preferences.
What Are the Key Nutrients in White Bread?
White bread nutrition includes several key nutrients, many of which are added during the enrichment process. Here are the primary nutrients found in white bread:
- Carbohydrates: The main macronutrient in white bread, providing energy.
- Protein: Present in small amounts, contributing to muscle repair and growth.
- Iron: Often added to white bread to support red blood cell production.
- B Vitamins: Including thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and folic acid, which are essential for energy metabolism and cell function.
While these nutrients are beneficial, white bread lacks certain components found in whole grains, such as fiber and healthy fats. This is why it's important to consider the overall nutritional context when including white bread in your diet.
Can White Bread Be Part of a Balanced Diet?
Yes, white bread can be part of a balanced diet if consumed in moderation and paired with nutrient-dense foods. For example, adding avocado, lean protein, or vegetables to white bread can enhance its nutritional value. This combination provides healthy fats, protein, and fiber, creating a more balanced meal.
It's also important to consider portion sizes. Consuming excessive amounts of white bread can lead to an overconsumption of refined carbohydrates, which may negatively impact blood sugar levels and overall health. Moderation is key to enjoying white bread without compromising your dietary goals.
What Are the Health Risks of White Bread?
While white bread nutrition offers some benefits, there are potential health risks associated with its overconsumption. The high glycemic index of white bread can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, which may increase the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes over time.
Additionally, the low fiber content can lead to digestive issues such as constipation. Fiber is essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, and its absence in white bread can disrupt digestive health. To mitigate these risks, it's advisable to limit white bread intake and opt for whole-grain alternatives whenever possible.
How to Choose Healthier White Bread Options?
If you prefer white bread, there are ways to choose healthier options. Look for bread labeled as "enriched" or "fortified," as these contain added nutrients. Additionally, check the ingredient list for whole grains or seeds, which can enhance the bread's nutritional profile.
Here are some tips for selecting healthier white bread:
- Choose bread with fewer added sugars.
- Opt for bread with higher fiber content, even if it's not whole grain.
- Look for bread fortified with additional vitamins and minerals.
What Are Some Alternatives to White Bread?
If you're looking to reduce your white bread intake, there are several nutritious alternatives available. Whole-grain bread, sprouted bread, and sourdough are excellent options that offer higher fiber and nutrient content. These alternatives can provide more sustained energy and better digestive health.
Other alternatives include:
- Gluten-free bread for those with gluten sensitivities.
- Low-carb bread for individuals following a ketogenic diet.
- Veggie wraps or lettuce wraps for a low-calorie option.
Why Is Fortification Important in White Bread Nutrition?
Fortification plays a crucial role in enhancing white bread nutrition. By adding essential vitamins and minerals, manufacturers can help address potential nutrient deficiencies in the population. For example, folic acid fortification has been instrumental in reducing the risk of neural tube defects in newborns.
Fortification ensures that even individuals who rely heavily on white bread can still meet their daily nutrient requirements. This practice highlights the importance of food science in improving public health outcomes.
What Experts Say About White Bread Nutrition?
Nutrition experts often emphasize the importance of moderation and balance when it comes to white bread nutrition. While it may not be the most nutrient-dense option, it can still be included in a healthy diet when paired with other nutritious foods. Experts recommend focusing on overall dietary patterns rather than individual food items.
Additionally, experts highlight the role of fortification in improving white bread's nutritional profile. By understanding these perspectives, you can make informed choices about incorporating white bread into your diet.
Everything You Need To Know About 150 Amp Service Wire Size
Understanding The Right Wire Gauge For 100 Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding The Key Differences Between Ponds And Lakes
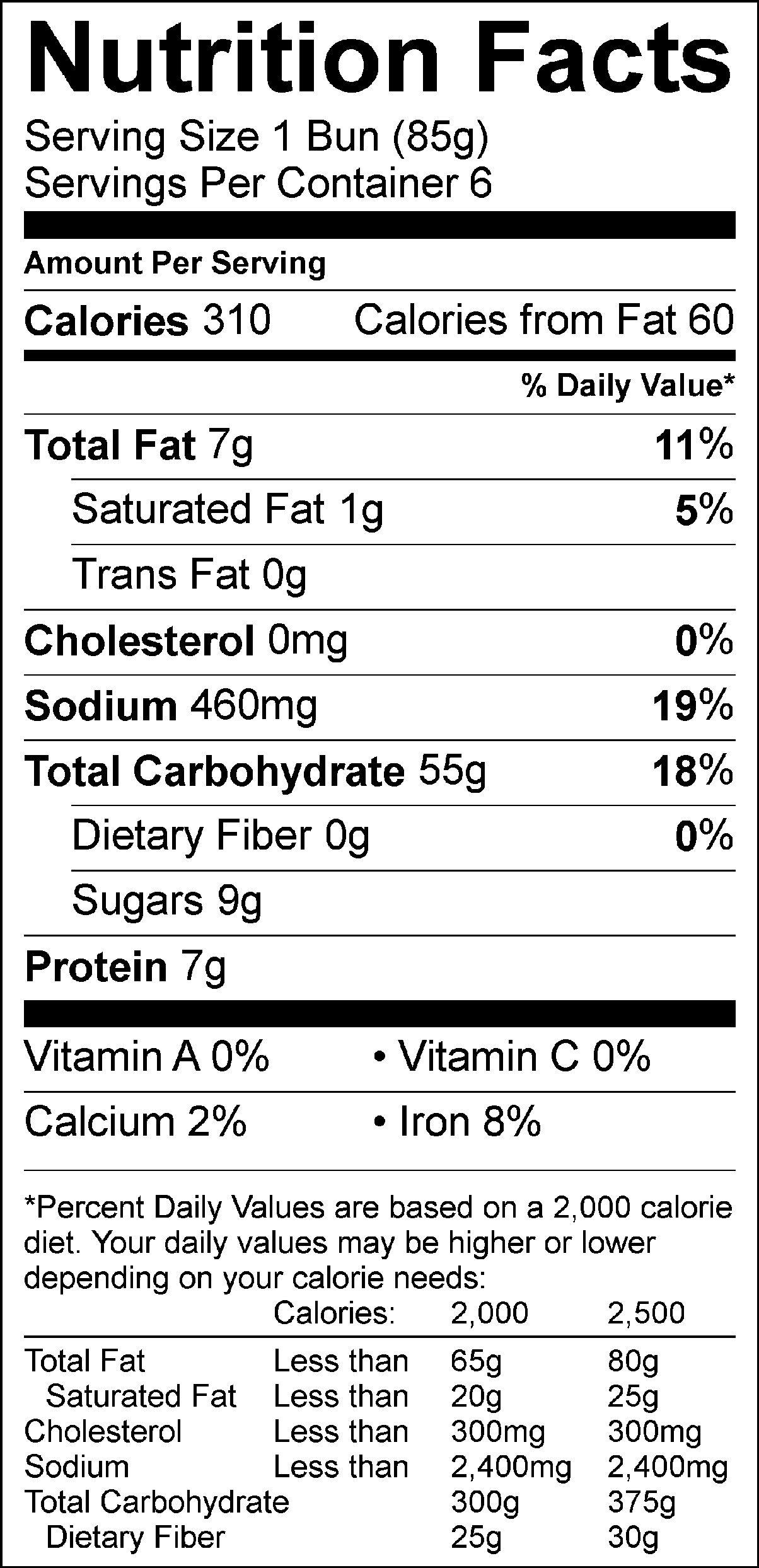
White Bread Nutrition Label Blog Dandk
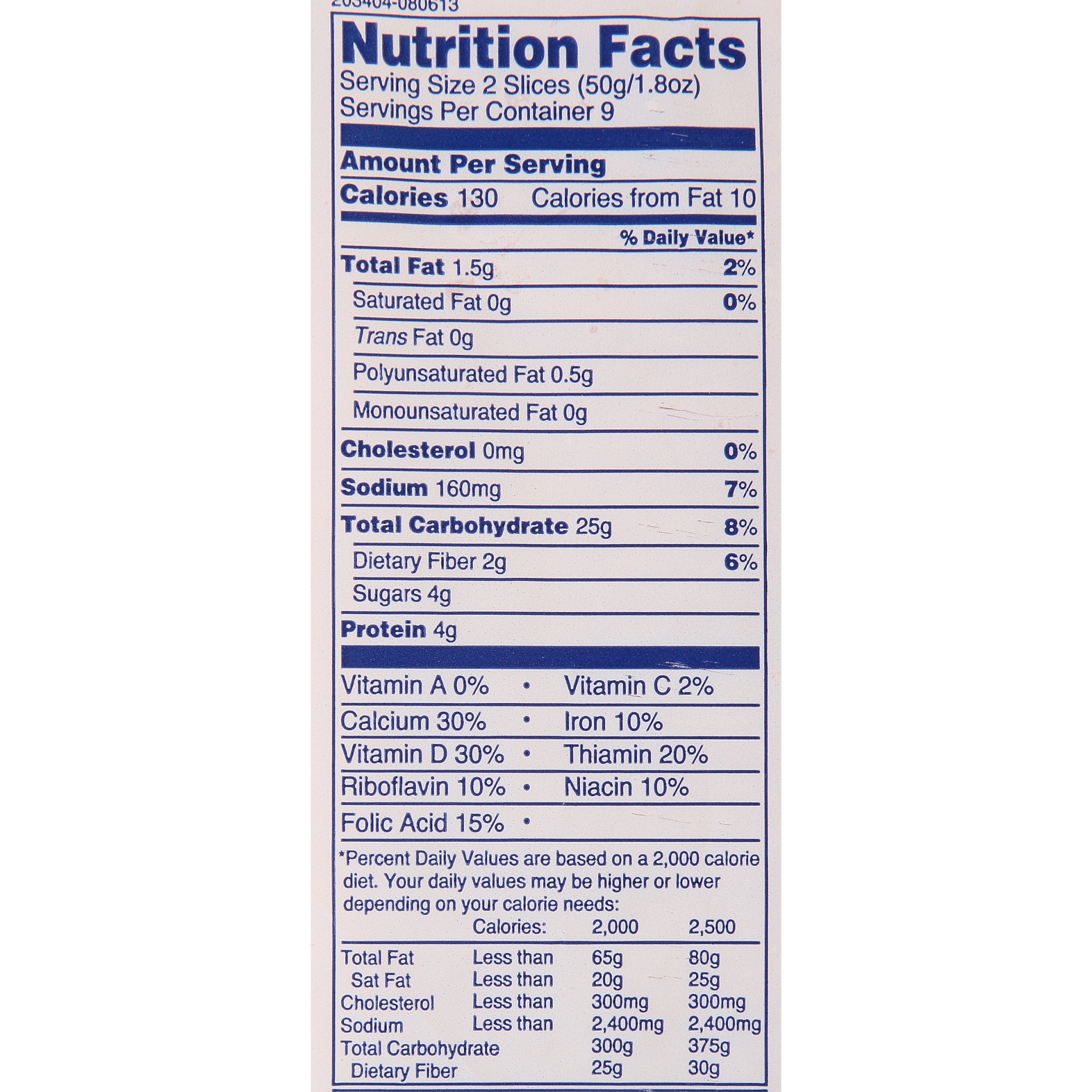
Wonder White Bread Nutrition Label Besto Blog