Choosing The Right Wire Size For 100 Amps: A Complete Guide
When it comes to electrical installations, choosing the correct wire size is crucial for safety and efficiency. For a 100-amp service, the right wire size ensures that your electrical system operates without overheating or causing fire hazards. Many homeowners and electricians often ask, "What size wire is good for 100 amps?" The answer depends on several factors, including the type of wire, the distance it needs to cover, and the material it is made of. Understanding these factors is essential to making an informed decision.
Electrical systems are the backbone of modern homes, and improper wiring can lead to costly repairs or dangerous situations. Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for electrical wiring, each with its own advantages and limitations. Copper wires are more conductive, which means they can carry more current with less resistance. Aluminum wires, on the other hand, are lighter and more cost-effective. To ensure your 100-amp service is reliable, you need to know how these materials influence the wire size you should choose.
Additionally, the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines to help you select the appropriate wire gauge for your needs. These guidelines are designed to ensure safety and compliance with local regulations. While the NEC recommendations are a great starting point, factors like voltage drop over long distances and environmental conditions can also impact your decision. Let’s dive deeper into the details to help you determine the best wire size for your 100-amp service.
Read also:Does Hwang In Yeop Have A Wife Unveiling The Truth About The Rising Star
Table of Contents
What Size Wire is Good for 100 Amps?
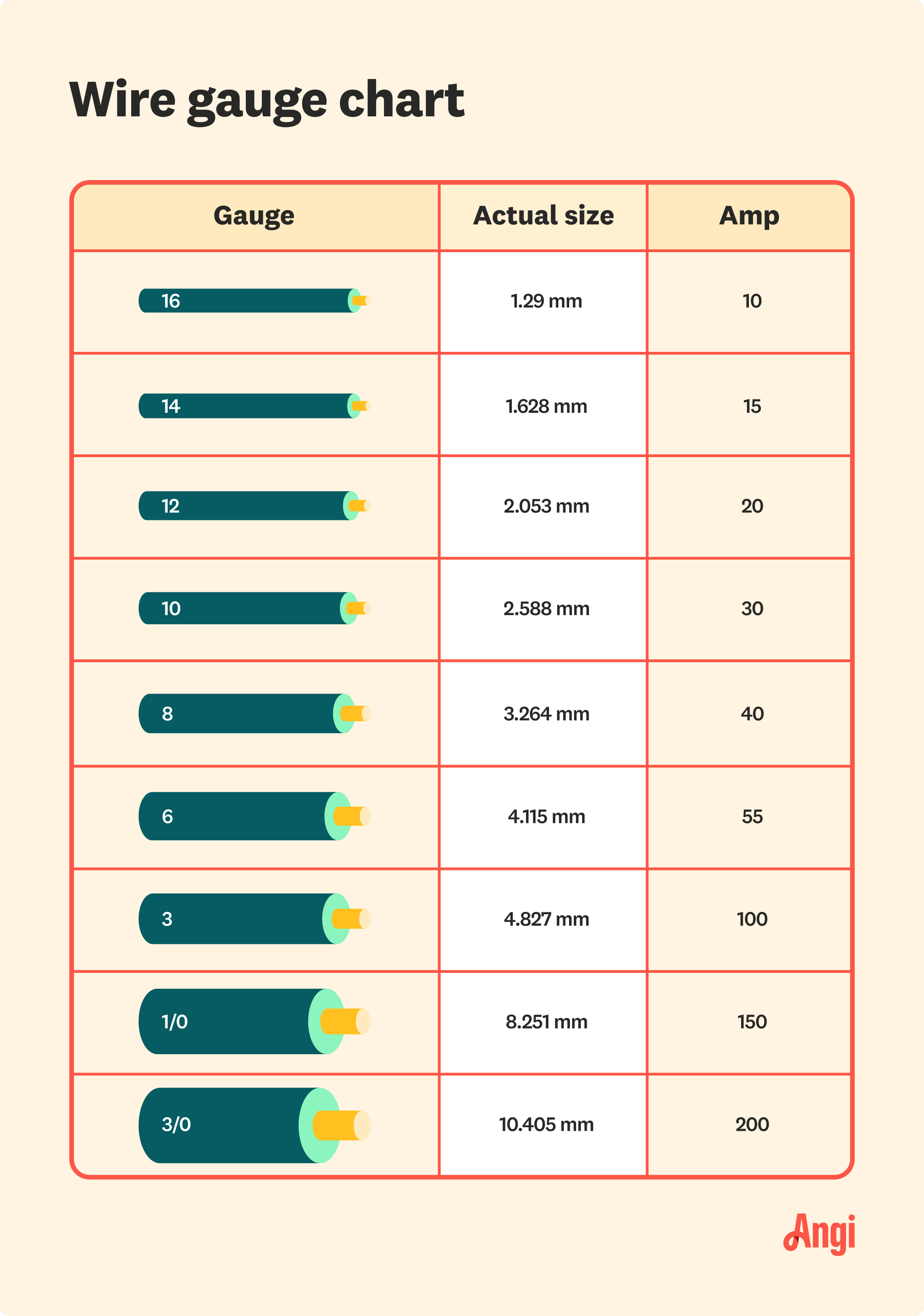
For a 100-amp service, the most commonly recommended wire size is 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum. These sizes are based on the NEC guidelines and are designed to handle the current load safely. However, it's important to note that these recommendations may vary depending on the specific application and local building codes.
When selecting the wire size, you must consider the type of insulation. For example, THHN/THWN wires are commonly used for residential wiring because they are heat-resistant and suitable for both dry and wet environments. Using wires with the correct insulation ensures that they can handle the current load without degrading over time.
Another factor to consider is whether the wire will be installed in conduit or free air. Wires in conduit may require a larger gauge to account for heat buildup. Always consult with a licensed electrician to ensure that your wire size meets all safety standards and local regulations.
How to Choose the Right Wire Size?
Choosing the right wire size involves more than just matching the amperage. You need to consider the load, the distance, and the environment where the wire will be installed. Here are some steps to guide you:
- Step 1: Determine the total load your circuit will carry. This includes all appliances, lighting, and devices connected to the circuit.
- Step 2: Check the NEC guidelines for the minimum wire size required for your load.
- Step 3: Consider the distance between the power source and the load. Longer distances may require a larger wire size to prevent voltage drop.
- Step 4: Choose the appropriate material (copper or aluminum) based on your budget and project requirements.
- Step 5: Verify that your chosen wire size complies with local building codes and regulations.
Why Does Wire Material Matter?
The material of the wire plays a significant role in determining its size and performance. Copper and aluminum are the two primary materials used in electrical wiring, and each has distinct characteristics.
Copper is more conductive than aluminum, which means it can carry more current with less resistance. This makes it ideal for high-load applications. However, copper is more expensive and heavier, which can make it less practical for large-scale projects.
Read also:Discovering The Journey Of Zeo Perry A Rising Star Worth Watching
Aluminum, on the other hand, is lighter and more affordable. While it is less conductive than copper, it is still widely used in residential and commercial wiring. To compensate for its lower conductivity, aluminum wires are typically larger in diameter than copper wires for the same current load.
What Are the NEC Guidelines?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides a comprehensive set of standards for electrical installations. These guidelines ensure that wiring is safe, efficient, and compliant with industry standards. For a 100-amp service, the NEC recommends the following wire sizes:
- Copper: 2 AWG
- Aluminum: 1/0 AWG
These recommendations are based on the assumption that the wire will be installed in a standard environment with no extreme conditions. If your project involves unusual circumstances, such as high temperatures or long distances, you may need to adjust the wire size accordingly.
How Does Distance Affect Wire Size?
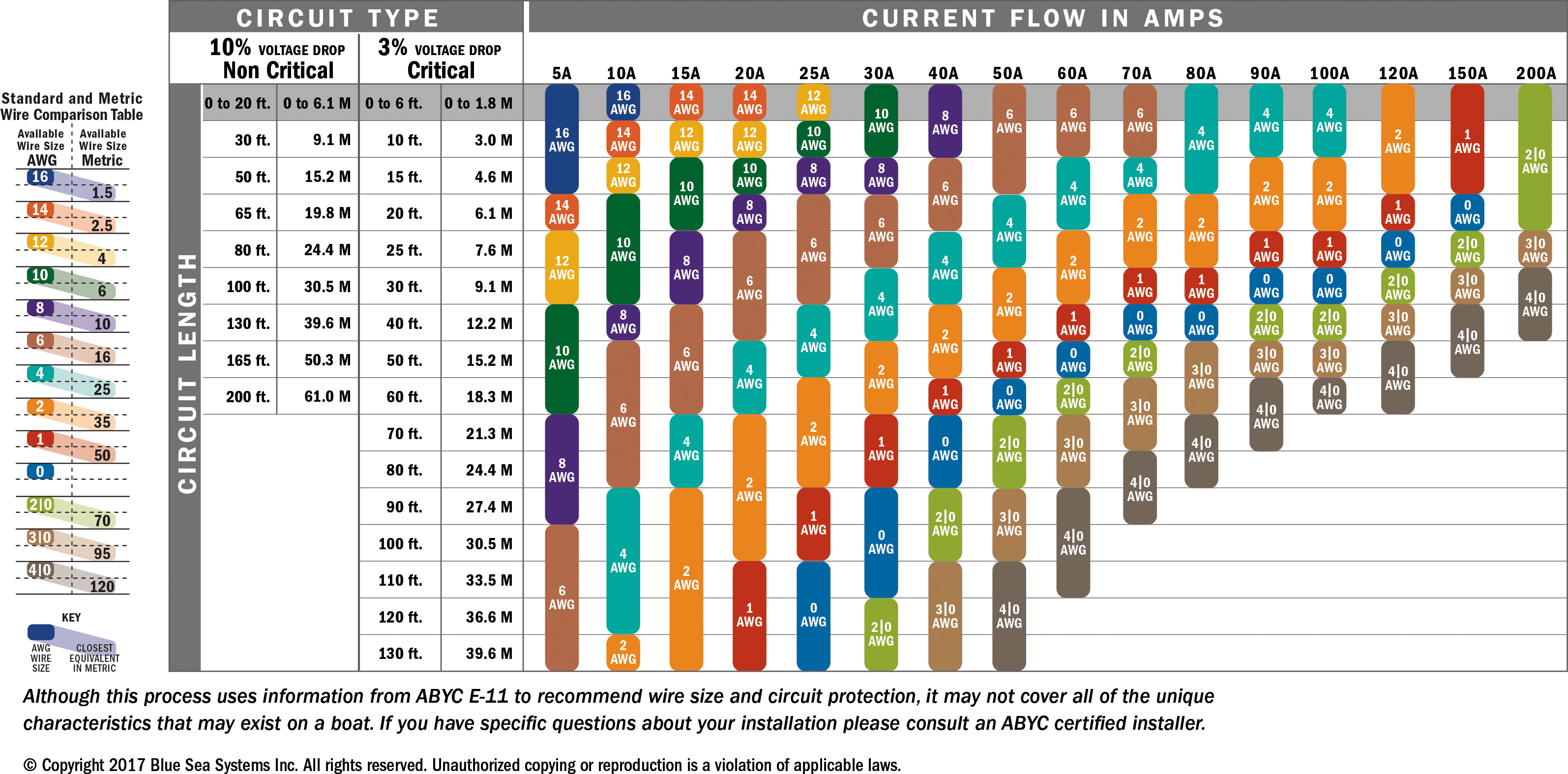
Distance is a critical factor when determining the appropriate wire size for your 100-amp service. As the distance between the power source and the load increases, the resistance in the wire also increases. This can lead to voltage drop, which reduces the efficiency of your electrical system.
To prevent voltage drop, you may need to use a larger wire size for longer distances. For example, if your 100-amp service is located more than 100 feet from the main panel, you may need to upgrade to a 1 AWG copper wire or a 2/0 AWG aluminum wire. Always calculate the voltage drop before finalizing your wire size to ensure optimal performance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When selecting and installing wires for a 100-amp service, there are several common mistakes that you should avoid:
- Using undersized wires: This can lead to overheating and fire hazards.
- Ignoring voltage drop: Failing to account for voltage drop can reduce the efficiency of your electrical system.
- Not consulting a professional: Electrical work should always be performed by a licensed electrician to ensure safety and compliance.
- Using incorrect insulation: Wires with improper insulation may degrade over time, leading to potential hazards.
Is Copper Better Than Aluminum?
Both copper and aluminum have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two depends on your specific needs. Copper is generally considered better for high-load applications due to its superior conductivity. However, aluminum is a more cost-effective option for large-scale projects.
Ultimately, the decision comes down to your budget, the application, and the local building codes. If you're unsure which material to choose, consult with a licensed electrician for guidance.
What About Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop occurs when the resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels from the source to the load. This can lead to inefficient operation of appliances and devices. To minimize voltage drop, you may need to use a larger wire size or reduce the distance between the power source and the load.
The NEC recommends that voltage drop should not exceed 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeder circuits. Always calculate the voltage drop for your specific installation to ensure that your electrical system operates efficiently.
How to Install Wires Safely?
Proper installation is just as important as choosing the right wire size. Here are some tips to ensure safe and efficient installation:
- Turn off the power: Always turn off the main power supply before working on electrical systems.
- Use proper tools: Use insulated tools and equipment to prevent electrical shocks.
- Follow NEC guidelines: Ensure that your installation complies with NEC standards.
- Hire a professional: If you're unsure about any aspect of the installation, consult with a licensed electrician.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What size wire is good for 100 amps?
A: For a 100-amp service, the recommended wire size is 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum, based on NEC guidelines.
Q: How does wire material affect wire size?
A: Copper is more conductive than aluminum, so it can carry the same current with a smaller diameter. Aluminum wires are typically larger to compensate for their lower conductivity.
Q: Can I use a smaller wire size for a 100-amp service?
A: No, using a smaller wire size can lead to overheating and fire hazards. Always follow NEC guidelines for safety.
Q: How do I calculate voltage drop?
A: Voltage drop can be calculated using the formula: Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000. Consult with a professional if you're unsure.
Understanding The Role Of Calories In Bread: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding The Calorie Content In Bread: A Comprehensive Guide
Vinila Gift.com: Your Ultimate Destination For Unique And Thoughtful Gifts
What Is the Correct Wire Size for 100Amp Service? Angi
What Size Wire For 90 Amps