What Wire Gauge For 100 Amps: A Comprehensive Guide
Whether you're wiring a new home, upgrading an existing electrical panel, or working on an industrial project, understanding the appropriate wire gauge can prevent overheating, reduce energy loss, and protect your property from potential hazards. A 100-amp service is a common electrical setup for many residential and commercial applications, but the wire gauge you select must meet specific requirements to handle the load safely.
Electrical systems rely on proper wire sizing to maintain optimal performance. Using a wire that is too small for the current it needs to carry can lead to overheating, which may cause fires or damage to your appliances. On the other hand, selecting a wire that is unnecessarily large can increase costs and make installation more cumbersome. For a 100-amp circuit, factors such as the length of the wire run, the material (copper or aluminum), and the ambient temperature all play a critical role in determining the right wire gauge.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about selecting the correct wire gauge for 100 amps. From understanding the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines to addressing common questions like "What wire gauge for 100 amps is best for long-distance runs?" and "How does temperature affect wire gauge selection?", we’ve got you covered. By the end of this guide, you’ll have the knowledge to make an informed decision and ensure your electrical setup is both safe and efficient.
Read also:Who Is David Goggins Wife Unveiling The Woman Behind The Ultraathlete
- What is Wire Gauge?
- Why Does Wire Gauge Matter for 100 Amps?
- What Wire Gauge for 100 Amps is Recommended?
- How to Choose the Right Wire for 100 Amps?
- Factors Affecting Wire Gauge Selection
- Can You Use Aluminum Wire for 100 Amps?
- What Are the Risks of Using the Wrong Wire Gauge for 100 Amps?
- How to Calculate Wire Length for 100 Amps?
- What Are the NEC Guidelines for 100 Amps?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Gauge for 100 Amps
What is Wire Gauge?
Wire gauge refers to the diameter of the wire, which determines its ability to carry electrical current. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is the standard used in the United States to classify wire sizes. The lower the AWG number, the thicker the wire and the greater its current-carrying capacity. For example, a 1-gauge wire is much thicker than a 10-gauge wire and can handle more current.
Understanding wire gauge is crucial because it directly impacts the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. Using a wire with an incorrect gauge can lead to overheating, voltage drop, or even electrical fires. For a 100-amp service, selecting the appropriate gauge ensures that the wire can handle the current without excessive heat buildup.
Why Does Wire Gauge Matter for 100 Amps?
When dealing with a 100-amp circuit, the wire gauge matters because it determines how much current the wire can safely carry. Electrical current generates heat, and if the wire is too small for the load, it can overheat and become a fire hazard. Additionally, an undersized wire can cause voltage drop, leading to inefficient operation of connected devices.
For example, if you use a wire gauge that is too small for a 100-amp circuit, the resistance in the wire increases, causing energy loss in the form of heat. This not only wastes electricity but also reduces the lifespan of your appliances. Therefore, understanding the importance of wire gauge for 100 amps is vital for maintaining a safe and efficient electrical system.
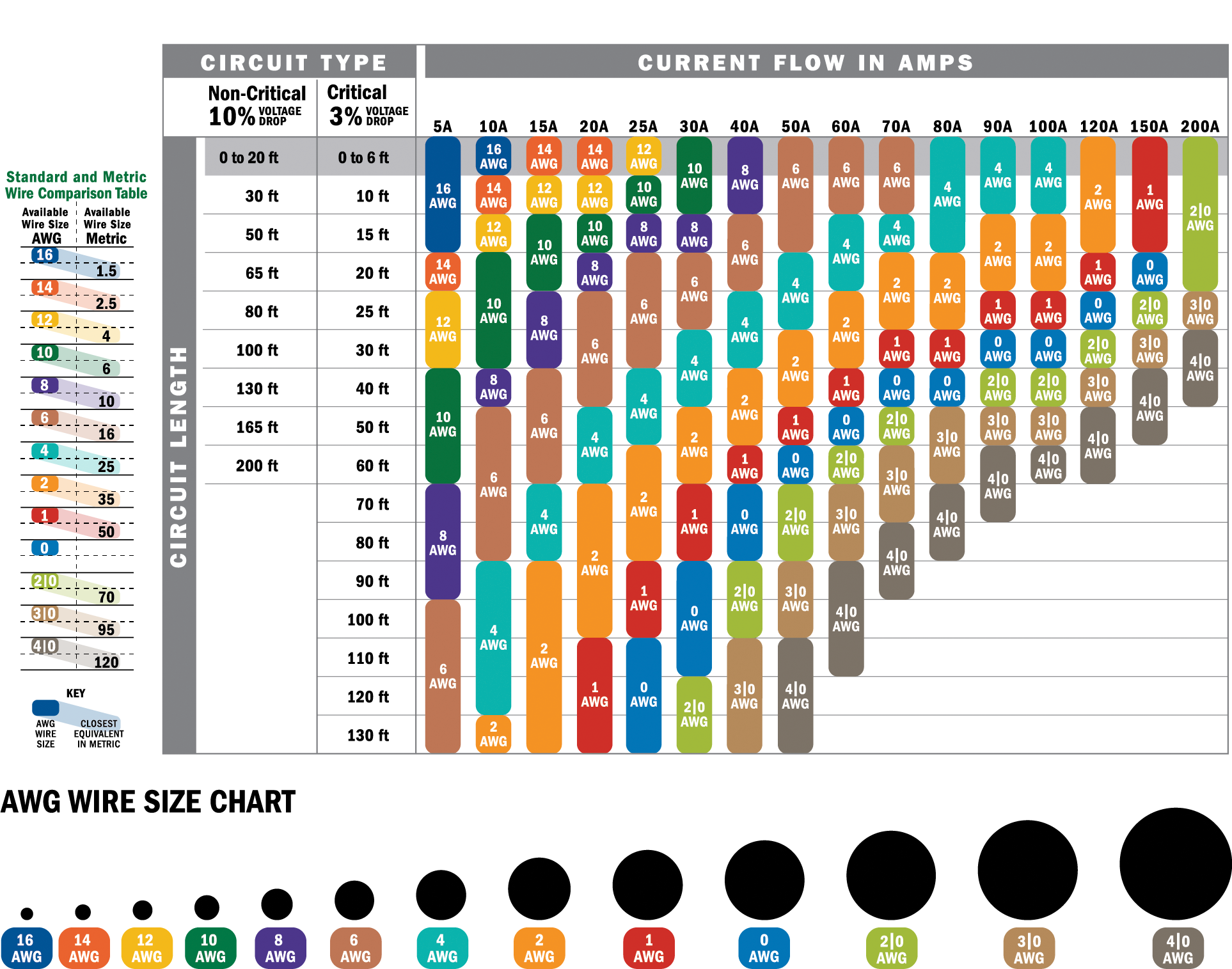
What Wire Gauge for 100 Amps is Recommended?
The recommended wire gauge for a 100-amp service depends on the material of the wire and the length of the run. For copper wires, a 2-gauge wire is typically sufficient for most residential applications. However, if you're using aluminum wire, you'll need a larger gauge, such as 1/0 (pronounced "one-aught"), due to aluminum's lower conductivity compared to copper.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the recommended wire gauges for 100 amps:
Read also:Who Was Amy Winehouses Last Partner And What Made Their Relationship So Intriguing
- Copper Wire: 2-gauge
- Aluminum Wire: 1/0-gauge
These recommendations are based on standard conditions. If your installation involves long distances or extreme temperatures, adjustments may be necessary.
How to Choose the Right Wire for 100 Amps?
Selecting the right wire for a 100-amp circuit involves considering several factors. First, determine whether you’ll use copper or aluminum wire. Copper is more conductive and durable but tends to be more expensive. Aluminum, while less costly, requires a larger gauge to achieve the same current-carrying capacity.
Next, consider the length of the wire run. Longer runs require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop. Finally, check the ambient temperature where the wire will be installed. High temperatures can reduce a wire's current-carrying capacity, necessitating a larger gauge.
Factors Affecting Wire Gauge Selection
Several factors influence the selection of wire gauge for a 100-amp circuit:
- Material: Copper vs. aluminum
- Length of Run: Longer runs require thicker wires
- Temperature: Higher ambient temperatures may require larger gauges
- Type of Insulation: Different insulation materials have varying temperature ratings
Understanding these factors ensures that you choose the correct wire gauge for 100 amps and avoid potential hazards.
Can You Use Aluminum Wire for 100 Amps?
Yes, you can use aluminum wire for a 100-amp circuit, but it requires careful consideration. Aluminum is less conductive than copper, so you’ll need a larger gauge to handle the same current. For example, a 1/0-gauge aluminum wire is equivalent to a 2-gauge copper wire for 100 amps.
Additionally, aluminum wire is more prone to corrosion and requires special connectors to ensure a secure connection. If you’re unsure about using aluminum wire, consult a licensed electrician for guidance.
What Are the Risks of Using the Wrong Wire Gauge for 100 Amps?
Using the wrong wire gauge for a 100-amp circuit can have serious consequences. An undersized wire can overheat, leading to fires or damage to your electrical system. It can also cause voltage drop, which affects the performance of your appliances and increases energy costs.
On the other hand, using a wire that is too large for the load can lead to unnecessary expenses and installation challenges. Therefore, it’s crucial to select the correct wire gauge for 100 amps based on your specific needs.
How to Calculate Wire Length for 100 Amps?
Calculating the wire length for a 100-amp circuit involves determining the acceptable voltage drop for your application. The general rule is to keep the voltage drop below 3% for optimal performance. To calculate the required wire gauge, use the following formula:
Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000
Where:
- Length: Distance of the wire run in feet
- Current: Load in amps (100 amps in this case)
- Resistance: Resistance per 1,000 feet of wire
By plugging in the values, you can determine the appropriate wire gauge for your specific application.
What Are the NEC Guidelines for 100 Amps?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for selecting wire gauges based on current-carrying capacity. According to the NEC, a 2-gauge copper wire or a 1/0-gauge aluminum wire is suitable for a 100-amp service under standard conditions. However, these guidelines may vary depending on factors such as temperature and wire insulation type.
Always consult the latest NEC edition and local building codes to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Gauge for 100 Amps
Here are some common questions and answers related to wire gauge for 100 amps:
- What wire gauge for 100 amps is best for long-distance runs? For long-distance runs, consider using a thicker wire, such as 1/0-gauge copper or 2/0-gauge aluminum, to minimize voltage drop.
- Can I use a 4-gauge wire for 100 amps? No, a 4-gauge wire is not suitable for a 100-amp circuit as it cannot safely handle the current load.
- How does temperature affect wire gauge selection? Higher temperatures reduce a wire's current-carrying capacity, so you may need a larger gauge in hot environments.
By addressing these questions, you can make informed decisions about wire gauge selection for your 100-amp circuit.
Discover The Best Spots For Tattoos: Your Ultimate Guide
What Does Enter Sandman Mean: Unpacking The Meaning Behind The Iconic Phrase
Genshin Impact Adepti: Unveiling The Secrets Of Teyvat's Mystical Beings
20 Gauge Wire Amps

Speaker wire gauge calculator vetkiza