Do Animals Have A Cell Membrane? Exploring The Science Of Life
Do animals have a cell membrane? This is a fascinating question that dives into the very essence of life itself. Every living organism, from the tiniest bacteria to the largest mammals, relies on cellular structures to survive and thrive. For animals, the cell membrane plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of their cells and ensuring proper functioning. This protective barrier is not just a passive layer; it actively regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell, making it indispensable for life. In this article, we will explore the science behind the cell membrane, its functions, and why it is so vital for animals.
Understanding the cell membrane is essential for grasping how animals function at a microscopic level. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a semi-permeable structure composed of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. It acts as a gatekeeper, allowing essential nutrients to enter the cell while expelling waste products. Without this critical barrier, cells would be unable to maintain homeostasis, leading to dysfunction and eventual death. This article will delve into the details of how the cell membrane operates and why it is a universal feature of animal cells.
The cell membrane is not unique to animals; it is found in all living organisms, including plants, fungi, and bacteria. However, the specific composition and functions of the cell membrane in animals differ slightly from those in other kingdoms. For instance, plant cells have an additional rigid cell wall that provides structural support, while animal cells rely solely on the flexibility of their cell membrane. This distinction highlights the adaptability of animal cells and their ability to thrive in diverse environments. Let’s explore the intricacies of the cell membrane and answer the question: do animals have a cell membrane?
Read also:Discovering Sean Gunn The Versatile Talent Behind The Camera And On Screen
Table of Contents
- What is a Cell Membrane?
- Do Animals Have a Cell Membrane?
- How Does the Cell Membrane Function?
- Why is the Cell Membrane Important for Animals?
- What Happens if the Cell Membrane is Damaged?
- How Does the Cell Membrane Differ in Animals and Plants?
- Do All Animals Have the Same Type of Cell Membrane?
- How Can We Study the Cell Membrane?
- What Are the Components of the Cell Membrane?
- Conclusion
What is a Cell Membrane?
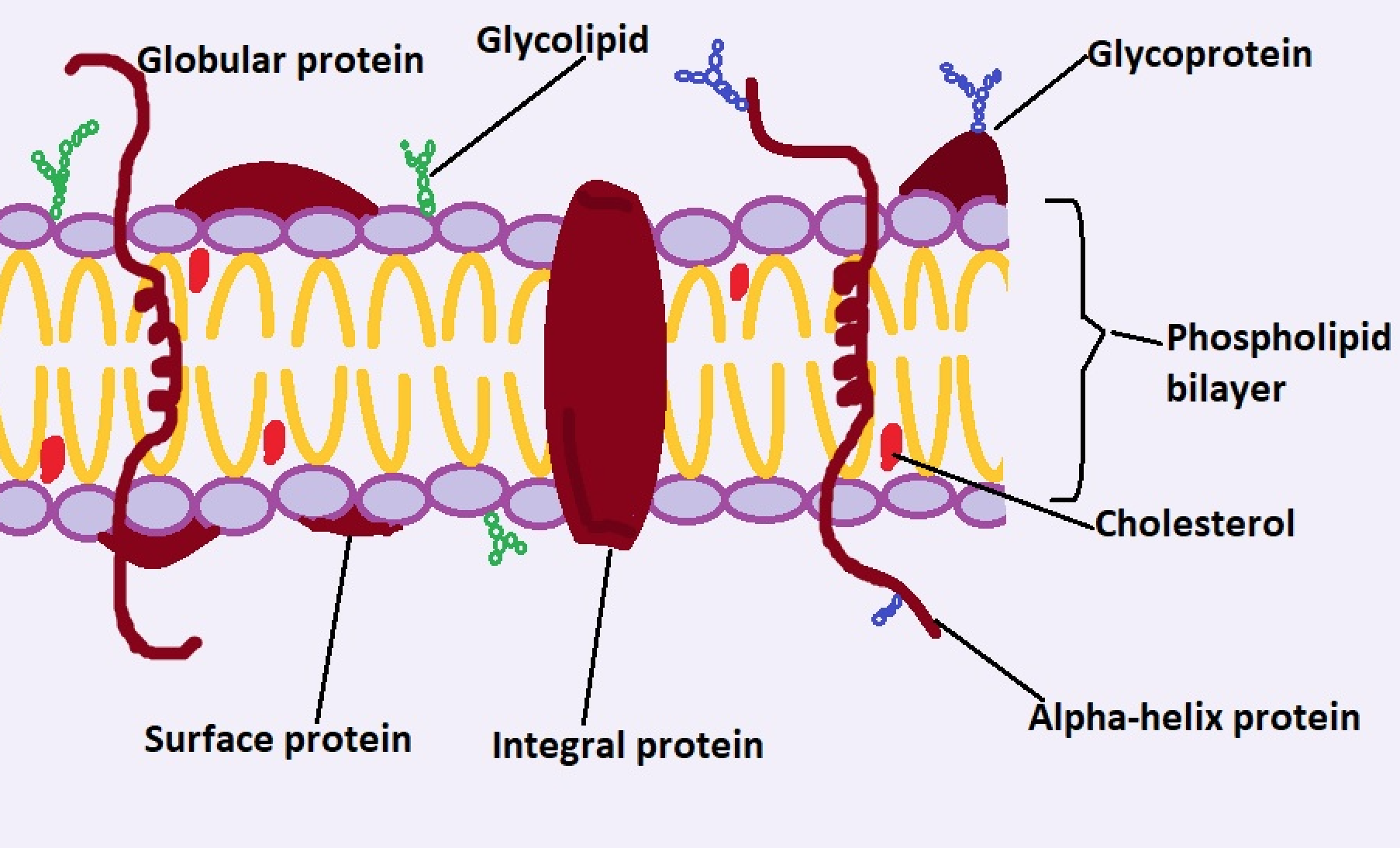
The cell membrane, also referred to as the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable yet dynamic structure. Embedded within this bilayer are proteins, cholesterol molecules, and carbohydrates, each playing a specific role in the membrane’s function. The cell membrane is selectively permeable, meaning it allows certain substances to pass through while blocking others. This selective permeability is essential for maintaining the internal environment of the cell.
The primary function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It acts as a barrier, shielding the cell’s internal components from harmful substances and pathogens. Additionally, the cell membrane facilitates communication between cells by housing receptor proteins that can detect external signals. This communication is crucial for processes such as immune response, hormone regulation, and nerve transmission.
Do Animals Have a Cell Membrane?
Yes, animals do have a cell membrane. In fact, the cell membrane is a universal feature of all animal cells. It serves as the boundary between the cell’s internal environment and the external world. Without the cell membrane, animal cells would be unable to regulate the movement of substances, leading to cellular dysfunction. The cell membrane in animals is composed of a lipid bilayer interspersed with proteins that perform various functions, such as transporting molecules and acting as receptors.
One of the key characteristics of the animal cell membrane is its fluidity. This fluidity allows the membrane to adapt to changing conditions, such as temperature fluctuations. The presence of cholesterol molecules within the membrane helps maintain this fluidity by preventing the lipids from packing too tightly. This adaptability is one of the reasons why animals can survive in a wide range of environments, from the freezing Arctic to the scorching deserts.
How Does the Cell Membrane Function?
The cell membrane functions through a combination of passive and active transport mechanisms. Passive transport, such as diffusion and osmosis, allows substances to move across the membrane without the use of energy. This process is driven by concentration gradients, where molecules move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. Active transport, on the other hand, requires energy in the form of ATP to move substances against their concentration gradient.
Proteins embedded in the cell membrane play a crucial role in these transport processes. For example, channel proteins create pores that allow specific molecules to pass through, while carrier proteins bind to molecules and change shape to transport them across the membrane. These mechanisms ensure that the cell receives the nutrients it needs while expelling waste products efficiently.
Read also:Czech Wife Swap New Exploring A Unique Lifestyle
Why is the Cell Membrane Important for Animals?
The cell membrane is vital for the survival of animals. It not only protects the cell but also enables it to interact with its environment. For instance, the cell membrane allows animals to respond to external stimuli, such as changes in temperature or the presence of predators. This responsiveness is made possible by receptor proteins that detect signals and initiate appropriate cellular responses.
Another critical function of the cell membrane is its role in maintaining homeostasis. By regulating the movement of ions and molecules, the membrane ensures that the cell’s internal environment remains stable. This stability is essential for processes such as enzyme activity, pH balance, and osmotic pressure. Without a functional cell membrane, animals would be unable to maintain the delicate balance required for life.
What Happens if the Cell Membrane is Damaged?
If the cell membrane is damaged, it can have severe consequences for the cell and the organism as a whole. A compromised membrane may lose its selective permeability, allowing harmful substances to enter the cell and essential nutrients to leak out. This disruption can lead to cellular dysfunction and, in severe cases, cell death.
Damage to the cell membrane can occur due to various factors, such as exposure to toxins, extreme temperatures, or mechanical injury. In animals, the immune system plays a crucial role in repairing damaged membranes and preventing infection. However, if the damage is extensive, the cell may undergo apoptosis, a programmed cell death process that prevents further harm to the organism.
How Does the Cell Membrane Differ in Animals and Plants?
While both animals and plants have cell membranes, there are some key differences between the two. Animal cell membranes are more flexible and lack the rigid structure found in plant cells. This flexibility allows animal cells to change shape and move, which is essential for processes such as muscle contraction and immune response.
In contrast, plant cells have an additional layer called the cell wall, which provides structural support and protection. The cell wall is composed of cellulose and is much thicker than the cell membrane. This difference in structure reflects the distinct roles of animal and plant cells in their respective organisms.
Do All Animals Have the Same Type of Cell Membrane?
While all animals have a cell membrane, the composition and properties of the membrane can vary depending on the species and cell type. For example, the cell membranes of cold-blooded animals, such as reptiles and amphibians, contain higher levels of unsaturated fatty acids to maintain fluidity at lower temperatures. In contrast, warm-blooded animals, such as mammals and birds, have membranes with a different lipid composition to withstand higher body temperatures.
Additionally, specialized cells, such as nerve cells and muscle cells, may have unique membrane properties to support their specific functions. These variations highlight the adaptability of the cell membrane and its ability to meet the needs of different organisms and cell types.
How Can We Study the Cell Membrane?
Scientists use a variety of techniques to study the cell membrane and its functions. One common method is electron microscopy, which allows researchers to visualize the membrane’s structure at a high resolution. This technique has provided valuable insights into the arrangement of lipids and proteins within the membrane.
Another approach is the use of fluorescent dyes and markers, which can be used to track the movement of molecules across the membrane. These tools enable scientists to study processes such as diffusion, osmosis, and active transport in real-time. Additionally, genetic engineering techniques can be used to manipulate membrane proteins, providing further insights into their roles and functions.
What Are the Components of the Cell Membrane?
The cell membrane is composed of three main components: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. The lipid bilayer forms the structural foundation of the membrane, providing a flexible and semi-permeable barrier. Proteins embedded in the membrane perform a variety of functions, such as transporting molecules, acting as receptors, and providing structural support.
Carbohydrates are attached to proteins and lipids on the outer surface of the membrane, forming glycoproteins and glycolipids. These carbohydrate chains play a crucial role in cell recognition and communication, allowing cells to interact with their environment and neighboring cells. Together, these components work in harmony to ensure the proper functioning of the cell membrane.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cell membrane is a vital component of all animal cells, playing a crucial role in maintaining cellular integrity and function. By regulating the movement of substances and facilitating communication, the cell membrane ensures that cells can survive and thrive in diverse environments. Whether you’re exploring the question, do animals have a cell membrane, or delving into the intricacies of its structure and function, the cell membrane is a fascinating topic that highlights the complexity of life at the cellular level.
Unwrapping The Sweetness Of Vanillagift.cpom: Your Ultimate Guide
Understanding The Challenges Of Wave Energy: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding CVV Amex: Everything You Need To Know

Cell Membrane In Plant Cell Or Animal Cell
Cell Membrane Function Simple