Exploring The Unique Characteristics Of Lakes And Ponds
Understanding the distinct characteristics of lakes and ponds is essential for anyone fascinated by natural water bodies. These freshwater ecosystems play a vital role in maintaining biodiversity and supporting life on Earth. Lakes and ponds characteristics vary widely depending on factors like size, depth, location, and surrounding environment. From their formation to their ecological significance, these water bodies offer endless opportunities for exploration and learning.
Lakes and ponds are more than just bodies of water; they are dynamic ecosystems teeming with life. While lakes are typically larger and deeper, ponds are smaller and shallower, which influences their temperature, light penetration, and the types of organisms they support. The characteristics of lakes and ponds are shaped by their unique hydrology, geology, and climate. These features determine how they interact with their surroundings and the role they play in the broader ecosystem.
Whether you're an environmental enthusiast, a student, or simply curious about nature, delving into the lakes and ponds characteristics can be both educational and inspiring. These water bodies are home to diverse flora and fauna, and their health directly impacts human communities. By understanding their unique traits, we can better appreciate their beauty and work toward their preservation for future generations.
Read also:Viral Insta Mms Video The Ultimate Guide To Understanding Its Impact
Table of Contents
- What Are the Main Characteristics of Lakes and Ponds?
- How Do Lakes and Ponds Differ in Size and Depth?
- What Role Do Lakes and Ponds Play in the Ecosystem?
- Why Are Lakes and Ponds Important for Biodiversity?
- How Are Lakes and Ponds Formed?
- What Are the Different Types of Lakes and Ponds?
- How Do Lakes and Ponds Characteristics Affect Water Quality?
- What Are the Common Threats to Lakes and Ponds?
- How Can We Protect Lakes and Ponds?
- What Can We Learn from Studying Lakes and Ponds?
What Are the Main Characteristics of Lakes and Ponds?
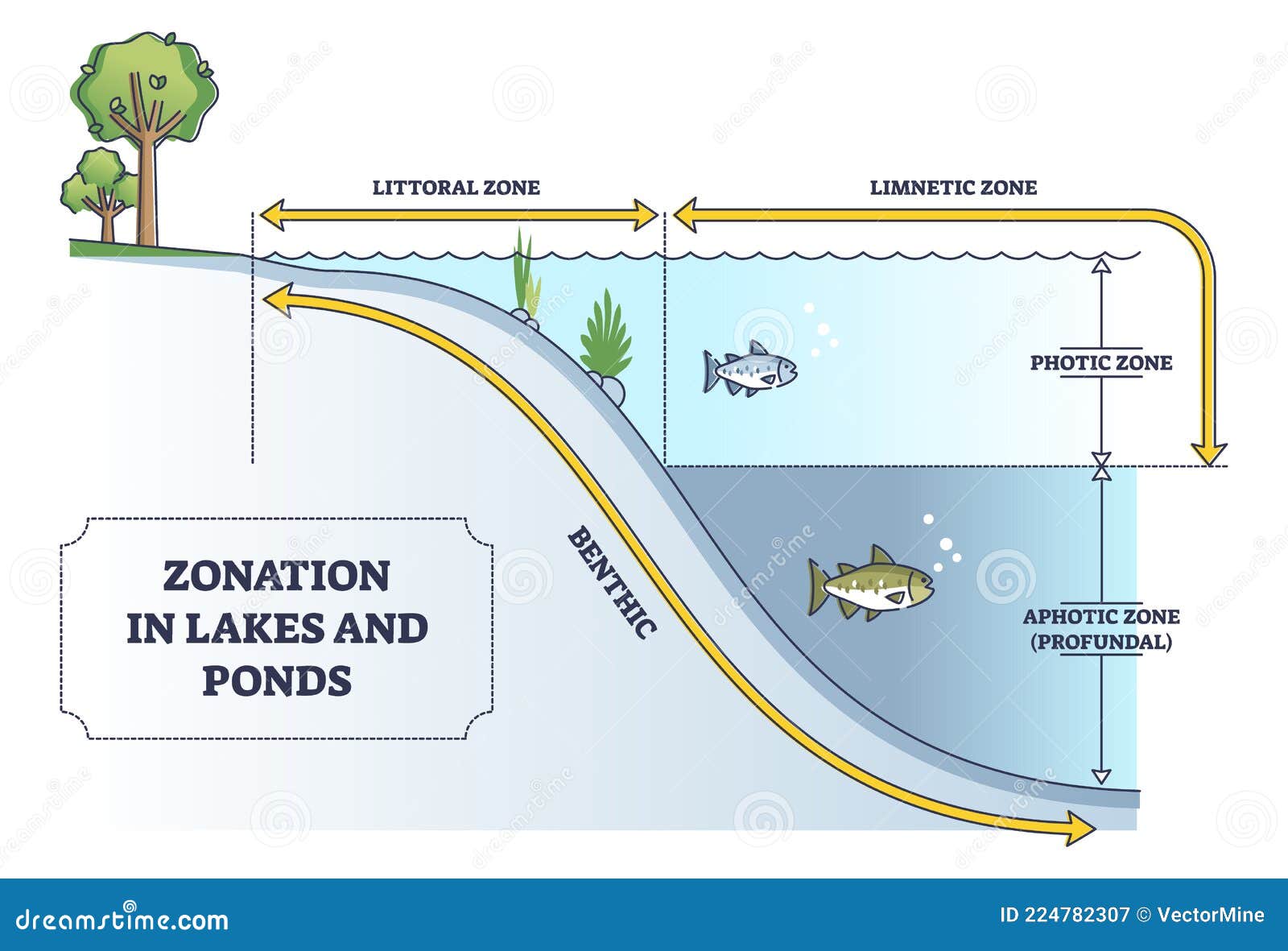
Lakes and ponds are defined by their physical, chemical, and biological characteristics. These features include their size, depth, temperature, nutrient levels, and the types of organisms they support. Lakes are generally larger and deeper than ponds, allowing for distinct zones such as the littoral, limnetic, and profundal zones. Ponds, on the other hand, are shallow enough for sunlight to penetrate to the bottom, supporting aquatic plants throughout.
One of the key lakes and ponds characteristics is their water clarity. Clear water indicates low levels of suspended particles and nutrients, while murky water suggests high nutrient levels, often leading to algal blooms. The temperature of these water bodies also varies with depth and season, influencing the types of fish and other organisms that can thrive in them.
Another important characteristic is the presence of dissolved oxygen, which is essential for aquatic life. In lakes, oxygen levels can vary significantly between the surface and deeper layers, especially in stratified systems. Ponds, being shallower, tend to have more uniform oxygen distribution, but they are also more susceptible to temperature fluctuations and pollution.
How Do Lakes and Ponds Differ in Size and Depth?
Size and depth are two of the most obvious differences between lakes and ponds. Lakes are typically larger and deeper, with surface areas exceeding several acres and depths reaching hundreds of feet. This allows them to support a wider range of aquatic life and create distinct ecological zones. Ponds, in contrast, are smaller and shallower, often covering less than an acre and having depths of only a few feet.
The depth of a water body affects its temperature and light penetration, which in turn influence its biological productivity. In lakes, the deeper areas may remain cold and dark year-round, creating a habitat for species adapted to low-light conditions. Ponds, being shallower, are more uniformly lit and warmer, promoting the growth of algae and aquatic plants.
These differences in size and depth also impact the water's ability to mix and circulate. Lakes often experience thermal stratification, where layers of water form based on temperature. Ponds, due to their smaller size, are more likely to mix completely, especially during seasonal changes like spring and fall turnovers.
Read also:Does Hwang In Yeop Have A Wife Unveiling The Truth About The Rising Star
What Role Do Lakes and Ponds Play in the Ecosystem?
Lakes and ponds are vital components of the Earth's ecosystem, providing habitat for countless species and serving as sources of freshwater for humans and wildlife. Their characteristics make them ideal environments for a wide range of organisms, from microscopic plankton to large fish and amphibians. These water bodies also play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and carbon storage, helping to regulate the planet's climate.
In addition to supporting biodiversity, lakes and ponds contribute to the livelihoods of millions of people. They are used for drinking water, irrigation, fishing, and recreation. The health of these ecosystems directly impacts the quality of life for nearby communities, making their conservation a priority.
Unfortunately, human activities such as pollution, deforestation, and climate change threaten the delicate balance of lakes and ponds characteristics. Protecting these ecosystems requires a comprehensive understanding of their functions and the challenges they face.
Why Are Lakes and Ponds Important for Biodiversity?
Lakes and ponds are hotspots of biodiversity, supporting a wide variety of plant and animal species. Their characteristics, such as nutrient availability and water clarity, determine the types of organisms that can thrive in these environments. From microscopic phytoplankton to large predators like fish and birds, these ecosystems are teeming with life.
The littoral zone, or shallow area near the shore, is particularly rich in biodiversity. This zone receives ample sunlight, allowing aquatic plants to grow and provide food and shelter for numerous species. The deeper zones of lakes, while less productive, are home to specialized organisms adapted to low-light and low-oxygen conditions.
Protecting the biodiversity of lakes and ponds is essential for maintaining the health of the broader ecosystem. These water bodies act as natural filters, purifying water and supporting the food web. Any disruption to their characteristics can have cascading effects on the species that depend on them.
How Are Lakes and Ponds Formed?
The formation of lakes and ponds is influenced by a variety of natural processes, including glacial activity, tectonic movements, volcanic eruptions, and erosion. Glacial lakes, for example, are created when glaciers carve out basins and melt, filling them with water. Tectonic lakes form in rift valleys or fault lines, while volcanic lakes are created in craters or calderas.
Ponds can also form through natural processes such as flooding, sediment deposition, or the activity of beavers. These smaller water bodies are often temporary, filling and drying with the seasons. Human activities, such as dam construction and excavation, can also create artificial lakes and ponds.
The characteristics of lakes and ponds are shaped by their formation process. For instance, glacial lakes tend to be deep and clear, while tectonic lakes may be saline due to high mineral content. Understanding these origins helps scientists predict how these ecosystems will respond to environmental changes.
What Are the Different Types of Lakes and Ponds?
Lakes and ponds can be classified based on their origin, size, depth, and water quality. Some common types include glacial lakes, tectonic lakes, oxbow lakes, and reservoirs. Each type has unique characteristics that influence its ecological functions and the species it supports.
For example, oxbow lakes are formed when a river changes course, leaving behind a U-shaped body of water. These lakes are often rich in nutrients and support diverse aquatic life. Reservoirs, on the other hand, are artificial lakes created by damming rivers, and their characteristics are heavily influenced by human management practices.
Ponds can also vary widely in their characteristics. Some are permanent, while others are seasonal. Permanent ponds often have more stable ecosystems, while seasonal ponds may experience dramatic changes in water levels and species composition.
How Do Lakes and Ponds Characteristics Affect Water Quality?
The characteristics of lakes and ponds have a direct impact on water quality. Factors such as nutrient levels, temperature, and oxygen content determine whether a water body is healthy or degraded. High nutrient levels, often caused by agricultural runoff or sewage, can lead to eutrophication, a process that depletes oxygen and harms aquatic life.
Temperature also plays a critical role in water quality. Warmer water holds less dissolved oxygen, making it difficult for fish and other organisms to survive. In lakes, thermal stratification can create oxygen-depleted zones in deeper layers, while ponds are more vulnerable to temperature fluctuations due to their shallowness.
Understanding the relationship between lakes and ponds characteristics and water quality is essential for effective management. By monitoring these factors, scientists can identify potential issues and implement strategies to protect these valuable ecosystems.
What Are the Common Threats to Lakes and Ponds?
Lakes and ponds face numerous threats from human activities and natural processes. Pollution, habitat destruction, invasive species, and climate change are among the most significant challenges. These threats can alter the characteristics of lakes and ponds, making them less hospitable for native species.
Pollution is one of the biggest threats to water quality. Nutrient runoff from agriculture, industrial waste, and sewage can lead to algal blooms and oxygen depletion. Habitat destruction, caused by activities like deforestation and urbanization, reduces the availability of food and shelter for aquatic organisms.
Climate change exacerbates these issues by altering temperature and precipitation patterns. Warmer temperatures can increase evaporation rates, reduce water levels, and disrupt the delicate balance of lakes and ponds characteristics. Addressing these threats requires coordinated efforts at local, national, and global levels.
How Can We Protect Lakes and Ponds?
Protecting lakes and ponds requires a combination of conservation, restoration, and sustainable management practices. Reducing pollution, restoring habitats, and controlling invasive species are key strategies for preserving these ecosystems. Public education and community involvement are also crucial for raising awareness and encouraging action.
One effective approach is to implement buffer zones around lakes and ponds. These vegetated areas help filter pollutants, reduce erosion, and provide habitat for wildlife. Restoring native vegetation and controlling runoff can also improve water quality and enhance biodiversity.
Governments and organizations play a vital role in protecting lakes and ponds through policies and regulations. By enforcing water quality standards and promoting sustainable practices, they can ensure the long-term health of these ecosystems.
What Can We Learn from Studying Lakes and Ponds?
Studying lakes and ponds provides valuable insights into the functioning of freshwater ecosystems and the impacts of human activities. These water bodies serve as natural laboratories, allowing scientists to observe ecological processes and test hypotheses about environmental change.
Research on lakes and ponds characteristics has led to important discoveries about nutrient cycling, climate change, and biodiversity. For example, studies of algal blooms have improved our understanding of how nutrient pollution affects water quality. Similarly, research on thermal stratification has shed light on the impacts of climate change on aquatic ecosystems.
By continuing to study lakes and ponds, scientists can develop innovative solutions to environmental challenges. This knowledge is essential for ensuring the sustainability of these vital ecosystems and the services they provide to humanity.
Exploring The Transformative Wave Energy Benefits For A Sustainable Future
Is Gel X Bad For You? Unveiling The Truth About Gel X Nails
Adeptus Genshin Impact: Unveiling The Mysteries Of Teyvat’s Divine Beings
Pictures Of Lakes And Ponds

How Do Lakes Differ from Ponds?