<strong>Exploring The Main Difference Between Ponds And Lakes: A Comprehensive Guide</strong>
When it comes to understanding the main difference between ponds and lakes, the distinction lies in their depth, size, and ecological characteristics. Ponds are typically smaller and shallower than lakes, which influences their ability to support aquatic life and maintain temperature stability. This fundamental difference shapes the ecosystems they harbor and the roles they play in the environment. Many people often confuse ponds and lakes due to their similar appearances, but the differences go far beyond surface-level observations. Knowing these differences can help us better appreciate the natural world and make informed decisions about water resource management.
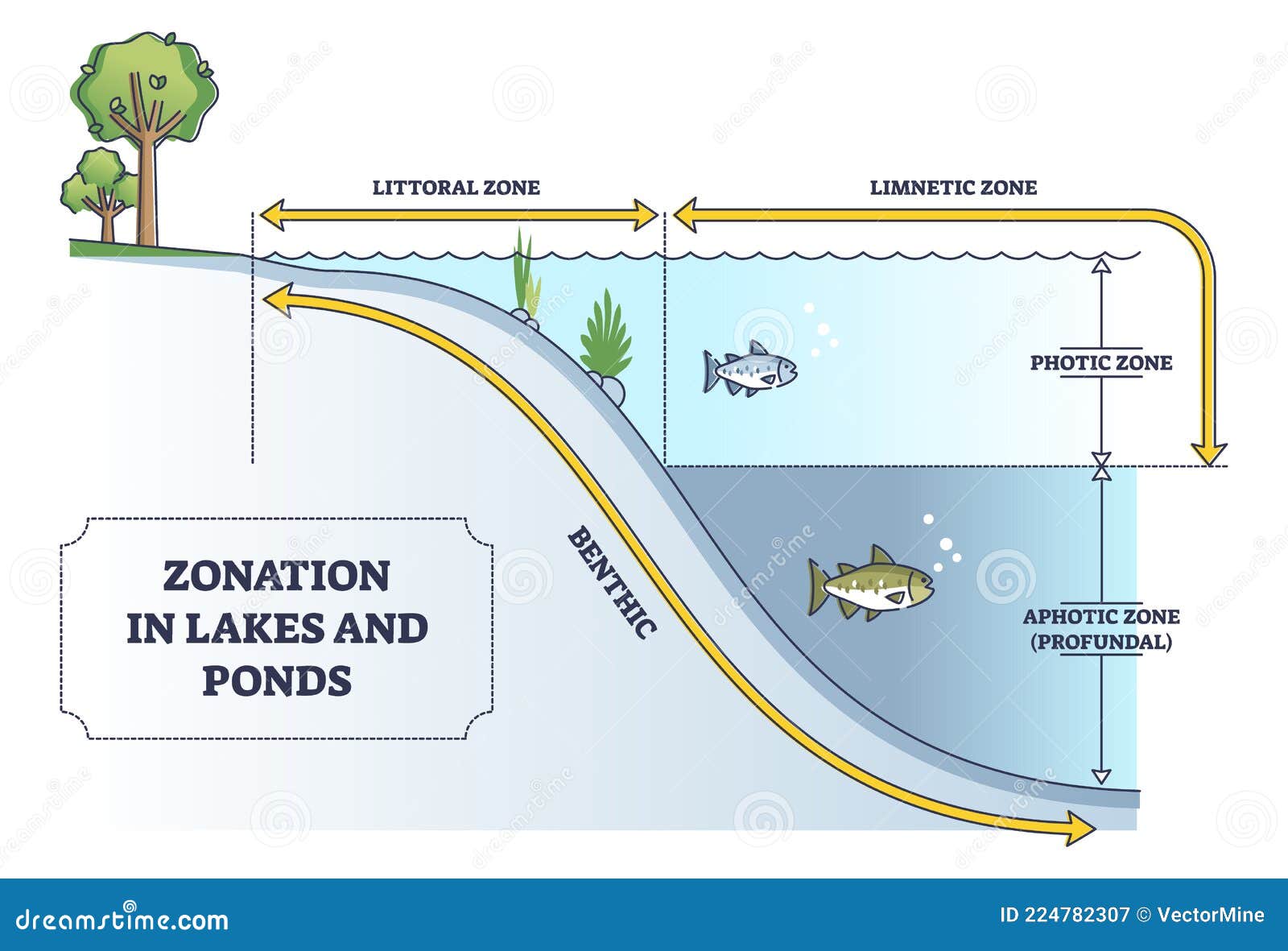
While ponds are often defined by their shallow depth, allowing sunlight to penetrate to the bottom and support rooted plants, lakes are deeper and often stratified, creating distinct temperature zones. These differences influence everything from the types of organisms that thrive in these water bodies to how humans interact with them. Whether you're a nature enthusiast, a student, or someone curious about aquatic ecosystems, understanding these distinctions is key to appreciating the complexity of freshwater systems.
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds are generally smaller and shallower, which directly impacts their temperature regulation and biodiversity. Lakes, on the other hand, are larger and deeper, creating unique habitats that support a wider range of aquatic life. This article will delve into these differences, explore their ecological implications, and provide insights into how these water bodies shape the world around us.
Read also:Couple Swap Czech Exploring Relationships And Lifestyle Choices
Table of Contents
- What Defines a Pond?
- How Do Lakes Differ from Ponds?
- Why Is the Main Difference Between Ponds and Lakes Important?
- Can Ponds Support the Same Aquatic Life as Lakes?
- How Do Ponds and Lakes Impact the Environment?
- What Are the Ecological Benefits of Ponds?
- What Makes a Lake Different in Terms of Depth?
- How Can You Identify a Pond Versus a Lake?
- What Role Do Ponds and Lakes Play in Climate Regulation?
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Defines a Pond?
Ponds are typically smaller and shallower water bodies that allow sunlight to reach their entire depth. This characteristic fosters an environment where rooted plants can thrive across the bottom. Ponds are often home to a variety of amphibians, insects, and small fish, making them vibrant ecosystems. Their smaller size also means they are more susceptible to temperature changes, which can influence the types of organisms that live there.
One key feature of ponds is their ability to support diverse plant life due to their shallow nature. This makes them excellent habitats for species like water lilies, cattails, and algae. Additionally, ponds often serve as breeding grounds for amphibians like frogs and salamanders, contributing to biodiversity. Understanding what defines a pond helps us appreciate its role in the environment and its unique ecological contributions.
How Do Lakes Differ from Ponds?
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds are generally smaller and shallower, while lakes are larger and deeper. Lakes often have stratified water layers, with distinct temperature zones that influence the types of organisms they can support. This depth and stratification make lakes more stable environments compared to ponds, which are more prone to fluctuations in temperature and water quality.
Lakes are also capable of supporting larger aquatic species, such as fish that require deeper waters to thrive. Their size and depth allow them to maintain cooler temperatures in deeper zones, even during warmer months. This stability makes lakes important for both biodiversity and human activities like fishing and recreation.
Why Is the Main Difference Between Ponds and Lakes Important?
Understanding the main difference between ponds and lakes is crucial for environmental management and conservation efforts. Ponds, with their shallow depths and diverse plant life, play a vital role in supporting local ecosystems. Lakes, on the other hand, are often critical water sources for communities and industries. Recognizing these differences helps us implement strategies to protect and preserve these valuable resources.
For example, ponds are often used for irrigation and as habitats for amphibians, while lakes are relied upon for drinking water and recreation. By understanding their unique characteristics, we can better manage these water bodies to ensure their sustainability for future generations.
Read also:Viral Mms World Unlocking The Secrets Of Digital Virality
Can Ponds Support the Same Aquatic Life as Lakes?
Ponds and lakes differ significantly in the types of aquatic life they can support. Ponds, being smaller and shallower, are ideal for species that thrive in warm, well-lit environments. This includes amphibians, small fish, and a variety of insects. However, larger fish that require deeper waters and cooler temperatures are more commonly found in lakes.
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds are often limited in their ability to support larger aquatic species. Lakes, with their greater depth and stability, provide habitats for a wider range of organisms, including predatory fish and migratory birds. This diversity makes lakes essential for maintaining balanced ecosystems.
How Do Ponds and Lakes Impact the Environment?
Ponds and lakes play vital roles in maintaining ecological balance. Ponds, with their rich plant life, help filter pollutants and improve water quality. They also serve as critical habitats for amphibians and insects, which are essential for food chains. Lakes, on the other hand, contribute to climate regulation by storing large amounts of water and carbon.
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds are often more localized in their impact, while lakes have broader environmental significance. Lakes can influence regional climates and serve as vital resources for human populations. Understanding their roles helps us appreciate their importance and take steps to protect them.
What Are the Ecological Benefits of Ponds?
Ponds offer numerous ecological benefits, from supporting biodiversity to improving water quality. Their shallow nature allows sunlight to penetrate the entire water column, fostering plant growth and creating habitats for amphibians and insects. Ponds also play a role in flood control by absorbing excess rainwater.
Additionally, ponds can serve as natural filters, trapping sediments and pollutants before they reach larger water bodies. This makes them valuable assets for maintaining healthy ecosystems and protecting downstream environments.
What Makes a Lake Different in Terms of Depth?
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that lakes are significantly deeper, which creates distinct temperature zones and influences their ecological dynamics. Lakes often have a thermocline, a layer where temperature changes rapidly with depth. This stratification supports diverse aquatic life and contributes to the lake's stability.
Deeper waters in lakes also allow for the development of unique habitats, such as cold-water zones for fish species like trout. This depth and stability make lakes critical for biodiversity and human use, from fishing to recreation.
How Can You Identify a Pond Versus a Lake?
Identifying a pond versus a lake can be challenging, but there are key indicators to look for. Ponds are generally smaller and shallower, allowing sunlight to reach the bottom and support rooted plants. Lakes, on the other hand, are larger and deeper, often with open water areas that lack vegetation.
Another way to distinguish between the two is by observing the types of organisms present. Ponds are often home to amphibians and small fish, while lakes support larger aquatic species. These differences highlight the main distinction between ponds and lakes and their unique ecological roles.
What Role Do Ponds and Lakes Play in Climate Regulation?
Ponds and lakes play significant roles in regulating the Earth's climate. Ponds, with their ability to absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, contribute to local air quality. Lakes, on the other hand, act as carbon sinks, storing large amounts of carbon and helping mitigate climate change.
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that lakes have a broader impact on regional climates due to their size and depth. Both water bodies are essential for maintaining ecological balance and supporting human activities, underscoring the need for their conservation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the main difference between ponds and lakes?
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds are smaller and shallower, allowing sunlight to penetrate the entire water column, while lakes are larger and deeper, creating distinct temperature zones.
2. Can ponds and lakes support the same types of aquatic life?
No, ponds are better suited for smaller species like amphibians and insects, while lakes support larger fish and migratory birds due to their depth and stability.
3. How do ponds and lakes benefit the environment?
Ponds improve water quality and support biodiversity, while lakes regulate climate and serve as vital water sources for human populations.
4. Why is it important to protect ponds and lakes?
Protecting these water bodies ensures the sustainability of ecosystems, supports biodiversity, and maintains their roles in climate regulation and human use.
Understanding Half Of 1/3 Cup: A Simple Guide For Everyday Cooking
Discover The Magic Of Vanillagigt.com: Your Ultimate Guide
How To Check Your Vanilla Gift Card .com Balance And Maximize Its Use

Lakes+Ponds Housatonic Heritage
Pictures Of Lakes And Ponds