Understanding The Vital Role Of Cell Membrane Function In An Animal Cell
What is the primary role of the cell membrane in an animal cell, and why is it so crucial to life itself? The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, serves as the gatekeeper of the cell, controlling what enters and exits. This semi-permeable barrier not only protects the cell’s internal environment but also plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis, communication, and energy production. For anyone interested in biology, understanding the cell membrane function in an animal cell is fundamental to grasping how cells operate and interact with their surroundings.
Every living organism relies on the functionality of its cells, and at the heart of cellular activity lies the cell membrane. This thin yet complex structure is composed of a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates, all working together to regulate cellular processes. By acting as a selective barrier, the cell membrane ensures that essential nutrients are absorbed while harmful substances are kept out, making it indispensable for survival. Its role in cell signaling and transport mechanisms also highlights its importance in maintaining the overall health of an organism.
From a scientific perspective, the cell membrane is more than just a protective layer. It actively participates in cellular communication, allowing cells to respond to external stimuli and interact with neighboring cells. This dynamic functionality enables processes such as immune response, nerve transmission, and hormone regulation. By exploring the intricacies of the cell membrane function in an animal cell, we gain deeper insights into how life operates at the microscopic level, making it a fascinating topic for both students and researchers alike.
Read also:Who Was Amy Winehouses Last Partner And What Made Their Relationship So Intriguing
- What is the Cell Membrane and Why is it Important?
- How Does the Cell Membrane Regulate Substances?
- What Are the Components of the Cell Membrane?
- Why is the Cell Membrane Semi-Permeable?
- How Does Cell Membrane Function Support Cell Signaling?
- Cell Membrane Function in Energy Production
- How Does the Cell Membrane Maintain Homeostasis?
- What Happens When the Cell Membrane is Damaged?
- The Role of the Cell Membrane in Immune Response
- Conclusion: The Importance of Cell Membrane Function
What is the Cell Membrane and Why is it Important?
The cell membrane is a vital structure that defines the boundaries of an animal cell. Without it, the cell would be unable to maintain its internal environment or interact effectively with its surroundings. Composed primarily of lipids and proteins, the membrane acts as both a physical barrier and a dynamic interface for cellular processes. Its semi-permeable nature allows it to regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell, ensuring that only essential molecules are permitted entry while waste products are expelled.
One of the key reasons why the cell membrane function in an animal cell is so critical is its role in maintaining homeostasis. This delicate balance of internal conditions is necessary for the cell to perform its functions efficiently. For example, the membrane helps regulate ion concentrations, pH levels, and water content, all of which are vital for cellular survival. Additionally, the membrane’s ability to facilitate communication between cells ensures that tissues and organs can work together harmoniously.
How Does the Cell Membrane Regulate Substances?
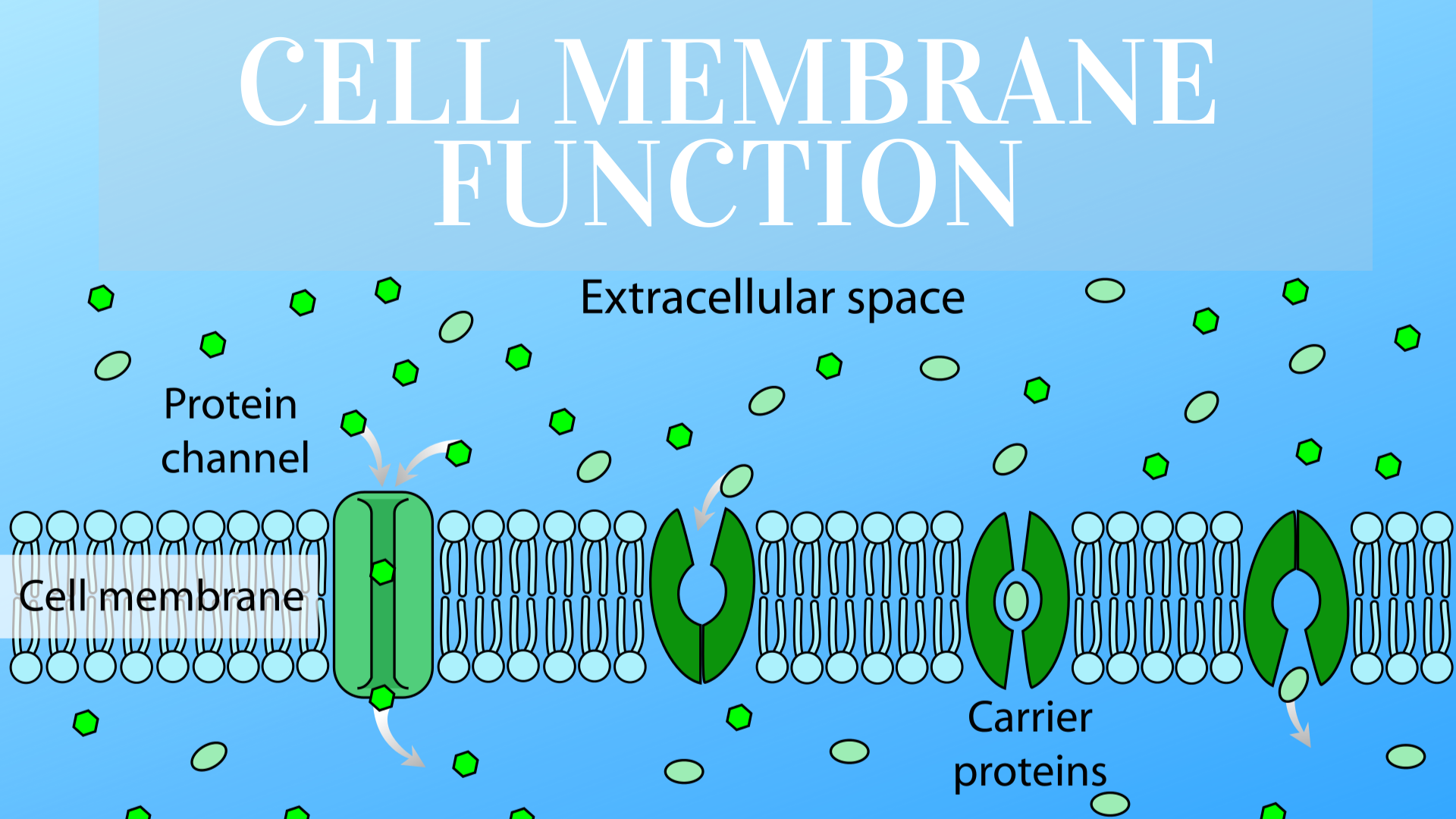
The regulation of substances is one of the most fascinating aspects of cell membrane function in an animal cell. This process occurs through various mechanisms, including passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, and endocytosis. Passive diffusion allows small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass freely through the lipid bilayer, while larger or charged molecules require specific transport proteins to cross the membrane.
Active transport, on the other hand, requires energy in the form of ATP to move substances against their concentration gradient. This is particularly important for maintaining ion gradients that are essential for nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction. Endocytosis and exocytosis are specialized processes that allow the cell to take in large particles or expel waste materials, further highlighting the versatility of the cell membrane in regulating cellular contents.
What Are the Components of the Cell Membrane?
The cell membrane is composed of several key components, each contributing to its overall functionality. The primary structure is the phospholipid bilayer, which consists of hydrophilic (water-attracting) heads and hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails. This arrangement creates a stable barrier that separates the cell’s interior from its external environment.
- Phospholipids: Form the basic framework of the membrane.
- Proteins: Embedded within the membrane, these proteins serve as channels, carriers, receptors, and enzymes.
- Cholesterol: Provides stability and fluidity to the membrane.
- Carbohydrates: Attached to proteins or lipids, they play a role in cell recognition and signaling.
Why is the Cell Membrane Semi-Permeable?
The semi-permeable nature of the cell membrane is one of its defining characteristics. This property allows the membrane to selectively permit certain substances to pass through while blocking others. For instance, water and small nonpolar molecules can diffuse freely, whereas larger molecules or ions require specific transport mechanisms.
Read also:Exploring The Life And Achievements Of Aneesha Joshi
This selective permeability is crucial for maintaining the cell’s internal environment. By controlling the movement of substances, the cell membrane function in an animal cell ensures that essential nutrients are absorbed, harmful substances are excluded, and waste products are removed efficiently. This balance is vital for the survival and proper functioning of the cell.
How Does Cell Membrane Function Support Cell Signaling?
Cell signaling is another critical function of the cell membrane in an animal cell. Embedded proteins in the membrane act as receptors that detect external signals, such as hormones or neurotransmitters, and relay this information to the cell’s interior. This process triggers a cascade of intracellular events that enable the cell to respond appropriately to its environment.
For example, when a hormone binds to its receptor on the cell membrane, it activates a signaling pathway that may lead to changes in gene expression, enzyme activity, or cellular movement. This ability to communicate and respond to external stimuli is essential for processes like growth, development, and immune response.
Cell Membrane Function in Energy Production
The cell membrane also plays a significant role in energy production, particularly in the context of cellular respiration. Specialized proteins embedded in the membrane, such as ATP synthase, are involved in the generation of ATP, the cell’s primary energy currency. These proteins are located in the mitochondria, which are enclosed by a double membrane system.
During oxidative phosphorylation, protons are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating a gradient that drives ATP synthesis. This process underscores the importance of the cell membrane function in an animal cell, as it directly contributes to the cell’s energy needs.
How Does the Cell Membrane Maintain Homeostasis?
Maintaining homeostasis is one of the primary responsibilities of the cell membrane. By regulating the movement of ions and molecules, the membrane ensures that the cell’s internal environment remains stable despite external fluctuations. This stability is essential for the proper functioning of enzymes, proteins, and other cellular components.
For instance, the sodium-potassium pump, a type of active transport mechanism, helps maintain the electrochemical gradient necessary for nerve impulse transmission. Similarly, aquaporins, which are water channels in the membrane, regulate water movement to prevent cellular dehydration or swelling.
What Happens When the Cell Membrane is Damaged?
Damage to the cell membrane can have severe consequences for the cell and the organism as a whole. A compromised membrane may lose its ability to regulate the movement of substances, leading to an imbalance in ion concentrations and water content. This can result in cellular dysfunction, swelling, or even cell death.
In certain diseases, such as autoimmune disorders or infections, the cell membrane may be targeted by pathogens or the immune system. Understanding the cell membrane function in an animal cell is therefore crucial for developing treatments that protect or repair this vital structure.
The Role of the Cell Membrane in Immune Response
The cell membrane plays a pivotal role in the immune response by facilitating the recognition of foreign invaders and initiating defense mechanisms. Specialized proteins on the membrane, such as major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, present antigens to immune cells, triggering an immune response.
This interaction between the cell membrane and the immune system highlights the membrane’s role in protecting the organism from pathogens. By acting as a first line of defense, the cell membrane helps safeguard the cell and the body from harm.
Conclusion: The Importance of Cell Membrane Function
In conclusion, the cell membrane function in an animal cell is indispensable for life. From regulating the movement of substances to facilitating communication and energy production, the membrane’s multifaceted role underscores its importance in cellular biology. By understanding its structure and function, we gain valuable insights into how cells operate and interact with their environment.
Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious about biology, exploring the intricacies of the cell membrane offers a deeper appreciation for the complexity of life at the microscopic level. As science continues to uncover new details about this remarkable structure, its significance in maintaining health and combating disease becomes increasingly clear.
Exploring The Benefits And Challenges Of Wave Power: A Comprehensive Guide
What Sets Lakes And Ponds Apart: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding The Difference
Understanding The Legal Age In Russia: A Comprehensive Guide

Cell Membrane Function In Plant Cell
Cell Membrane Definition And Function Functions Functions and Diagram