Understanding White Bread Nutrition Facts: A Comprehensive Guide
White bread is a staple in many households, but do you really know what's inside this popular food item? With its soft texture and versatile taste, white bread is often a go-to choice for sandwiches, toast, and more. However, understanding its nutritional profile is essential for making informed dietary choices. White bread nutrition facts reveal important details about its calorie content, macronutrient breakdown, and micronutrient composition, helping you determine how it fits into your daily diet.
Many people are unaware of the specific nutrients found in white bread, including carbohydrates, protein, and essential vitamins. While it may not be as nutrient-dense as whole grain alternatives, white bread is often fortified with key nutrients like iron and B vitamins. This makes it a valuable source of energy for those who rely on it as part of their meals. Learning more about white bread nutrition facts can empower you to balance your diet while still enjoying this classic food.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the nutritional aspects of white bread, answering common questions like "Is white bread healthy?" and "What are the key components of white bread nutrition facts?" We'll also explore how white bread compares to other bread types and provide tips for incorporating it into a balanced diet. Whether you're a health-conscious individual or simply curious about your food choices, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to make smarter decisions.
Read also:Couple Swap Czech Exploring Relationships And Lifestyle Choices
- What Are the Key White Bread Nutrition Facts?
- Is White Bread Healthy for You?
- How Does White Bread Compare to Other Breads?
- What Are the Health Benefits of White Bread?
- What Are the Drawbacks of White Bread?
- Can White Bread Be Part of a Balanced Diet?
- How Can You Make Better Choices with White Bread?
- What Are the Fortified Nutrients in White Bread?
- How Does White Bread Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
- Frequently Asked Questions About White Bread Nutrition Facts
What Are the Key White Bread Nutrition Facts?
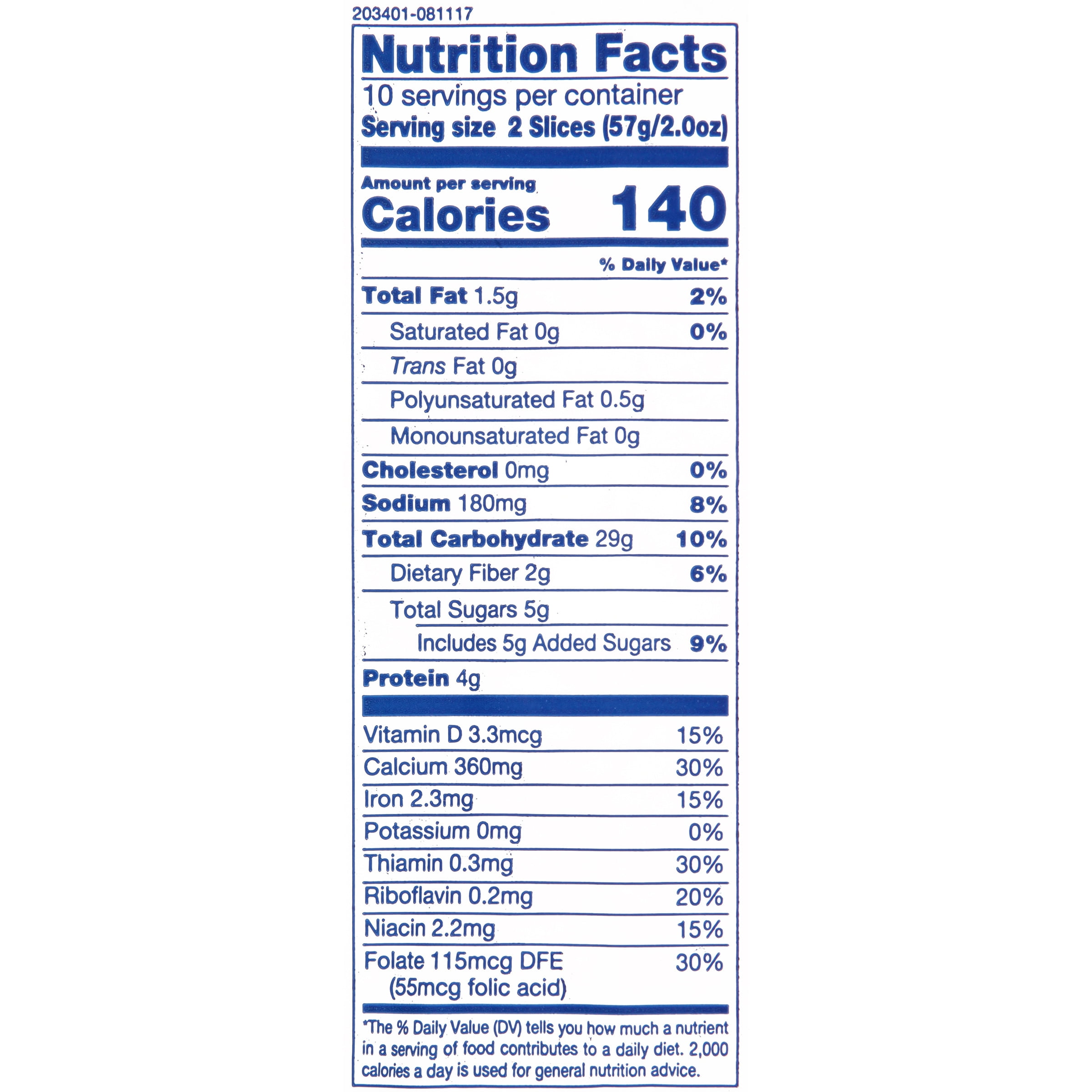
When examining white bread nutrition facts, it's important to break down its macronutrient composition. A standard slice of white bread (approximately 28 grams) typically contains around 70-80 calories, with the majority coming from carbohydrates. Carbs make up about 15 grams per slice, while protein contributes around 2-3 grams. Fat content is minimal, usually less than 1 gram per slice.
White bread is often enriched with essential vitamins and minerals, such as thiamine (vitamin B1), riboflavin (vitamin B2), niacin (vitamin B3), and folic acid. These nutrients play a crucial role in energy metabolism and red blood cell production. Additionally, iron is commonly added during the fortification process, making white bread a source of this vital mineral for individuals with dietary deficiencies.
What Makes White Bread Nutrition Facts Unique?
One of the standout features of white bread nutrition facts is its fortification. Unlike whole grain bread, which naturally contains fiber and nutrients from the bran and germ, white bread relies on added vitamins and minerals to enhance its nutritional value. This fortification process ensures that even though white bread is refined, it still provides essential nutrients that contribute to overall health.
Is White Bread Healthy for You?
The question of whether white bread is healthy depends on your dietary goals and lifestyle. While it may not be as nutrient-dense as whole grain options, white bread can still be part of a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. Understanding white bread nutrition facts allows you to assess its role in your meal plan.
What Are the Health Benefits of White Bread?
Despite its reputation, white bread offers several health benefits. Its high carbohydrate content serves as a quick source of energy, making it ideal for individuals who need a boost before physical activity. Additionally, the fortified nutrients in white bread, such as folic acid and iron, support overall health and well-being.
Does White Bread Nutrition Facts Support Weight Management?
For those managing their weight, portion control is key when consuming white bread. A single slice is relatively low in calories, but overeating can lead to excess calorie intake. Pairing white bread with nutrient-rich toppings like avocado, lean proteins, or vegetables can enhance its nutritional value and make it a satisfying meal option.
Read also:Who Is Zoe Perry A Comprehensive Look Into The Life Of A Rising Star
How Does White Bread Compare to Other Breads?
Comparing white bread to other types of bread, such as whole wheat or multigrain, reveals distinct differences in nutritional content. Whole grain options generally contain more fiber and naturally occurring nutrients, while white bread relies on fortification to boost its nutritional profile.
Why Do White Bread Nutrition Facts Differ from Whole Grain Breads?
The refining process used to make white bread removes the bran and germ, which are rich in fiber and nutrients. This results in a softer texture but reduces the natural nutrient content. However, the fortification process helps bridge the gap by adding essential vitamins and minerals back into the bread.
Which Bread Is Better for Digestive Health?
Whole grain breads are often preferred for digestive health due to their higher fiber content. Fiber promotes regular bowel movements and supports a healthy gut microbiome. While white bread nutrition facts show lower fiber levels, choosing fortified varieties can still provide some health benefits.
What Are the Drawbacks of White Bread?
While white bread has its advantages, it also comes with certain drawbacks that should be considered. Understanding these limitations can help you make informed decisions about including white bread in your diet.
Does White Bread Nutrition Facts Impact Blood Sugar Levels?
White bread has a high glycemic index, meaning it can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. This is due to its refined carbohydrates, which are quickly digested and absorbed by the body. Individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance should monitor their intake of white bread to avoid blood sugar fluctuations.
Can White Bread Lead to Overeating?
Because white bread is low in fiber and protein, it may not provide the same level of satiety as whole grain options. This can lead to overeating or frequent snacking, potentially contributing to weight gain if not managed properly.
Can White Bread Be Part of a Balanced Diet?
Absolutely! White bread can fit into a balanced diet when consumed mindfully. By pairing it with nutrient-dense foods, you can enhance its nutritional value and enjoy it as part of a healthy eating plan.
How Can You Incorporate White Bread Nutrition Facts into a Healthy Lifestyle?
One way to include white bread in your diet is by using it as a base for nutritious meals. For example, top a slice with almond butter and banana slices for a balanced snack, or use it to make a sandwich filled with lean protein, vegetables, and hummus. These combinations provide additional nutrients and help keep you full longer.
How Can You Make Better Choices with White Bread?
Making better choices with white bread starts with reading labels and understanding white bread nutrition facts. Look for varieties that are fortified with essential nutrients and avoid those with added sugars or unhealthy fats.
What Should You Look for on White Bread Nutrition Labels?
When shopping for white bread, check the ingredient list for whole grains or enriched flour. Opt for breads with minimal added sugars and a good balance of fortified nutrients. This ensures you're getting the most nutritional value from your purchase.
What Are the Fortified Nutrients in White Bread?
Fortified nutrients in white bread include B vitamins like thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and folic acid, as well as iron. These additions are designed to compensate for the nutrients lost during the refining process.
Why Are Fortified Nutrients Important in White Bread?
Fortified nutrients play a vital role in maintaining overall health. For example, folic acid is essential for pregnant women to prevent neural tube defects in developing babies, while iron supports red blood cell production and prevents anemia.
How Does White Bread Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
White bread's high glycemic index means it can cause rapid increases in blood sugar levels. This effect is particularly important for individuals managing conditions like diabetes or prediabetes.
What Can You Do to Mitigate Blood Sugar Spikes from White Bread?
To reduce the impact of white bread on blood sugar, pair it with foods that contain protein, healthy fats, or fiber. These nutrients slow down digestion and absorption, helping to stabilize blood sugar levels.
Frequently Asked Questions About White Bread Nutrition Facts
Here are answers to some common questions about white bread nutrition facts:
- Is white bread bad for weight loss? Not necessarily, but portion control is important.
- How many calories are in a slice of white bread? Typically, a slice contains 70-80 calories.
- What vitamins are added to white bread? B vitamins and iron are commonly fortified.
By understanding white bread nutrition facts, you can make informed decisions about incorporating this food into your diet. Whether you're looking for quick energy or a convenient meal option, white bread can be a valuable part of your nutritional strategy when consumed wisely.
How To Master The Art Of Communication In Everyday Life?
Embracing Emoji: The Evolution Of Digital Communication
Understanding The Nutritional Value Of White Bread: A Comprehensive Guide
White Wonder Bread Nutrition Facts Besto Blog

Wonder Plus Bread Nutrition Facts Nutrition Ftempo