Understanding The Unique Zones Of Lakes: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring the diverse zones of a lake provides a fascinating glimpse into the intricate balance of aquatic ecosystems. The littoral, limnetic, and profundal zones each play a unique role in supporting life and maintaining the health of the lake environment. These zones are not only distinct in their physical characteristics but also in the types of organisms they support. Understanding how to distinguish among the littoral, limnetic, and profundal zones of lakes in is essential for anyone interested in freshwater ecosystems, whether you're a student, researcher, or nature enthusiast.
Each zone has its own defining features, from sunlight penetration to the types of plants and animals that thrive there. The littoral zone, for example, is the shallow area near the shore, where sunlight reaches the bottom and supports diverse plant life. Moving further into the lake, the limnetic zone is characterized by open water where light penetrates deeply, fostering plankton growth. Finally, the profundal zone lies in the deeper, darker parts of the lake, where light barely reaches and conditions are colder and less hospitable. Together, these zones create a dynamic and interconnected aquatic environment.
Learning to distinguish among the littoral, limnetic, and profundal zones of lakes in can deepen your appreciation for the complexity of freshwater systems. This knowledge is not only valuable for scientific study but also for conservation efforts, as understanding these zones can help in managing and protecting lake ecosystems. Whether you're exploring a lake for recreation or studying its ecological dynamics, recognizing these zones is key to understanding the lake's overall health and biodiversity.
Read also:Discovering Marshall Mathers A Deep Dive Into His Age And Legacy
- What Are the Different Zones of a Lake?
- How Can You Distinguish Among the Littoral, Limnetic, and Profundal Zones of Lakes In?
- What Organisms Thrive in the Littoral Zone?
- Why Is the Limnetic Zone Important for Lake Ecosystems?
- How Does the Profundal Zone Differ from Other Zones?
- The Role of Sunlight in Lake Zones
- Why Is Biodiversity Important in Lake Zones?
- How Do Human Activities Affect Lake Zones?
- What Are the Conservation Efforts for Lake Zones?
- How Can You Protect the Health of Lake Zones?
What Are the Different Zones of a Lake?
Lakes are divided into distinct zones based on factors such as sunlight penetration, depth, and the types of organisms that inhabit them. These zones include the littoral, limnetic, and profundal zones. Each zone has unique characteristics that contribute to the overall health and function of the lake ecosystem. Understanding these zones is crucial for studying aquatic life and managing water resources effectively.
How Can You Distinguish Among the Littoral, Limnetic, and Profundal Zones of Lakes In?
To distinguish among the littoral, limnetic, and profundal zones of lakes in, it's important to consider the depth and light availability. The littoral zone is the shallowest and most sunlight-rich area, often supporting rooted plants and diverse aquatic life. The limnetic zone, located farther from the shore, is deeper and supports plankton and free-floating organisms. The profundal zone, found in the deepest parts of the lake, is characterized by minimal light and colder temperatures, making it less hospitable to most life forms.
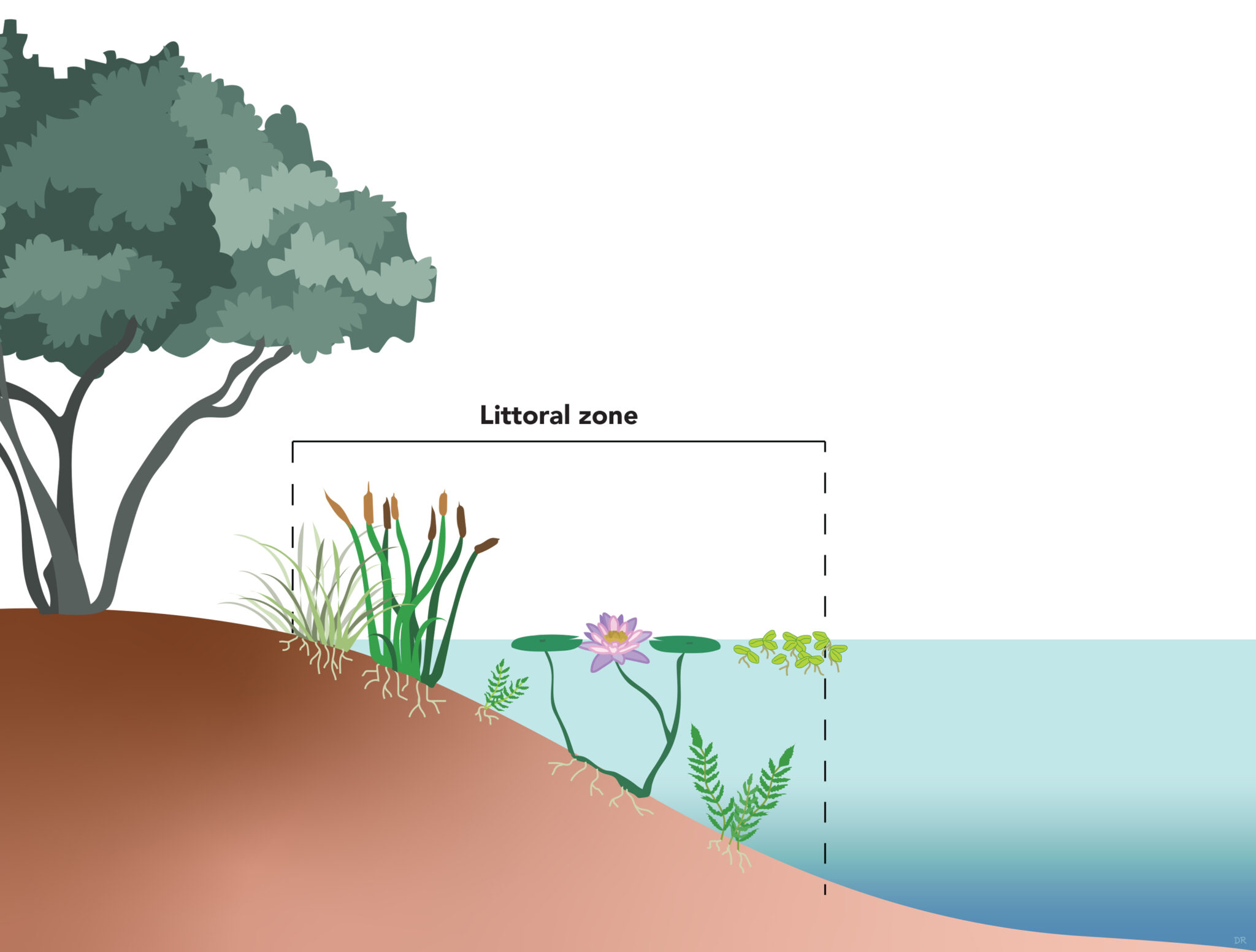
What Organisms Thrive in the Littoral Zone?
The littoral zone is teeming with life due to its abundant sunlight and nutrient-rich environment. Plants such as cattails, bulrushes, and water lilies thrive here, providing food and shelter for a variety of organisms. Fish like bass and bluegill, as well as amphibians, insects, and crustaceans, are commonly found in this zone. The biodiversity of the littoral zone makes it a critical area for the overall health of the lake.
Why Is the Limnetic Zone Important for Lake Ecosystems?
The limnetic zone is the open-water area of a lake, extending beyond the littoral zone. This zone is crucial for supporting plankton, which form the base of the aquatic food chain. Phytoplankton, in particular, play a vital role in producing oxygen through photosynthesis. The limnetic zone is also home to fish species that rely on plankton as a primary food source, making it a key area for maintaining the balance of the lake's ecosystem.
How Does the Profundal Zone Differ from Other Zones?
The profundal zone is the deepest part of the lake, where sunlight penetration is minimal or nonexistent. This zone is characterized by cold temperatures and low oxygen levels, creating a challenging environment for most organisms. However, certain species of bacteria and detritivores can survive here, breaking down organic matter that sinks from the upper zones. The profundal zone plays a vital role in nutrient cycling within the lake.
The Role of Sunlight in Lake Zones
Sunlight is a critical factor in distinguishing among the littoral, limnetic, and profundal zones of lakes in. The littoral zone receives the most sunlight, allowing plants to photosynthesize and create energy. In the limnetic zone, sunlight supports plankton growth, while the profundal zone receives little to no light, limiting biological activity. Understanding the role of sunlight helps explain the distribution of life across these zones.
Read also:Discovering Stephen Walters The Journey Of A Remarkable Personality
Why Is Biodiversity Important in Lake Zones?
Biodiversity is essential for the health and stability of lake ecosystems. Each zone supports different species, contributing to the overall balance of the ecosystem. For example, the littoral zone's diverse plant life provides habitat and food for numerous organisms, while the limnetic zone's plankton support fish populations. Protecting biodiversity ensures that these zones can continue to function effectively and sustain aquatic life.
How Do Human Activities Affect Lake Zones?
Human activities such as pollution, deforestation, and overfishing can have a significant impact on lake zones. Nutrient runoff from agriculture can lead to algal blooms in the littoral and limnetic zones, depleting oxygen levels and harming aquatic life. Overfishing can disrupt food chains, while climate change can alter water temperatures and affect species distribution. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing strategies to protect lake ecosystems.
What Are the Conservation Efforts for Lake Zones?
Conservation efforts for lake zones focus on reducing pollution, restoring habitats, and promoting sustainable practices. Initiatives such as wetland restoration, shoreline stabilization, and the implementation of buffer zones help protect the littoral zone. Reducing nutrient runoff and controlling invasive species are essential for maintaining the health of the limnetic and profundal zones. Public education and community involvement are also key components of successful conservation efforts.
How Can You Protect the Health of Lake Zones?
Individuals can play a vital role in protecting the health of lake zones by adopting eco-friendly practices. Reducing the use of fertilizers and pesticides, properly disposing of waste, and participating in lake cleanup events are simple yet effective ways to contribute. Supporting policies that promote sustainable water management and conservation is also important. By taking these steps, we can help ensure the long-term health and vitality of lake ecosystems.
In conclusion, distinguishing among the littoral, limnetic, and profundal zones of lakes in is essential for understanding the complex dynamics of freshwater ecosystems. Each zone plays a unique role in supporting life and maintaining ecological balance. By learning about these zones and taking steps to protect them, we can contribute to the preservation of these vital natural resources for future generations.
Is Fungi Autotrophic Or Heterotrophic? Unraveling The Mystery Of Fungal Nutrition
How Much Does It Cost To Live In Hawaii? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Calories In Bread: A Comprehensive Guide
Littoral Zone Plants Nature's WaterCleaning Wonders Naples

Brand Lakes Webflow