What Size Wire For 100 Amps: A Comprehensive Guide To Safe Electrical Wiring
Whether you're upgrading your electrical panel, installing a subpanel, or running new wiring for a home addition, knowing the right wire gauge is crucial. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about selecting the appropriate wire size for 100 amps, addressing common questions, and providing actionable advice.
Electrical systems are designed to handle specific loads, and the wire size plays a pivotal role in carrying the current safely. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for wire sizing, taking into account factors such as amperage, distance, and material type. Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for wiring, and each has its own requirements. While copper is more conductive and often preferred, aluminum is a cost-effective alternative for larger installations. Understanding these nuances will help you make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes.
In this article, we’ll explore the factors that influence wire size selection, answer frequently asked questions, and provide practical tips to ensure your electrical system operates safely and efficiently. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of what size wire for 100 amps is appropriate for your specific needs and how to implement it correctly. Let’s dive into the details and equip you with the knowledge to make the best choices for your electrical projects.
Read also:Table of ContentsDoes Hwang In Yeop Have A Wife Unveiling The Truth About The Rising Star
- What Size Wire for 100 Amps?
- Why Does Wire Size Matter?
- What Are the Common Wire Materials?
- How Far Can You Run 100 Amp Wire?
- Is Copper Better Than Aluminum?
- What Are the NEC Requirements?
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop?
- What Size Wire for 100 Amps Subpanel?
- What Are the Safety Tips?
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Size Wire for 100 Amps?
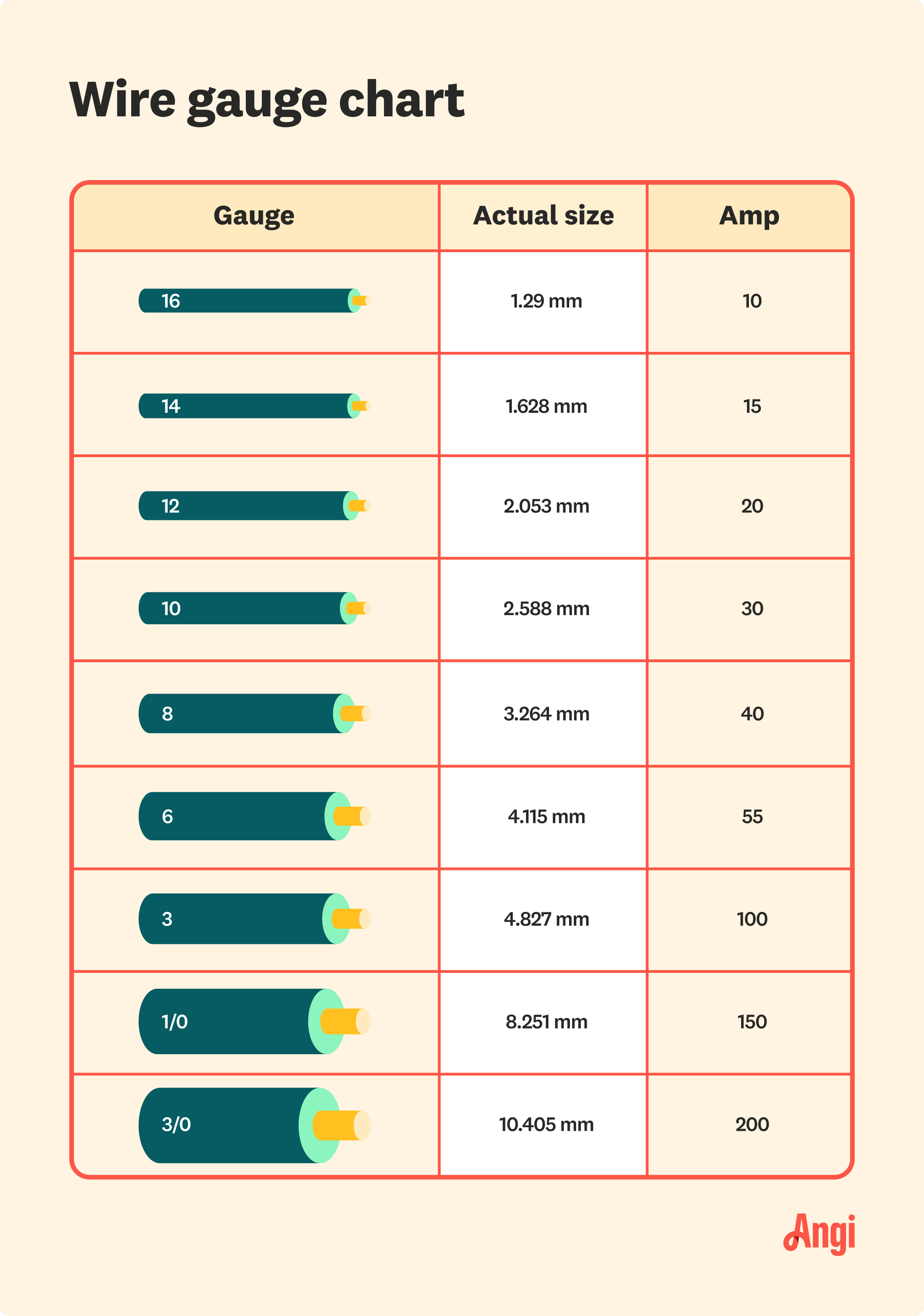
For a 100-amp electrical service, the recommended wire size is typically 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum. These sizes are based on the NEC guidelines and are designed to handle the current safely without overheating. Copper wires are more conductive, meaning they can carry the same amount of current with a smaller gauge compared to aluminum. However, aluminum wires are lighter and less expensive, making them a popular choice for long-distance runs or larger installations.
It’s important to note that wire size can vary depending on the length of the run and the type of insulation used. For example, if you’re running wire over a long distance, you may need to increase the wire size to compensate for voltage drop. Always consult the NEC tables or a licensed electrician to ensure compliance with local codes and safety standards.
Why Does Wire Size Matter?
The size of the wire directly impacts its ability to carry electrical current safely. If the wire is too small for the amperage it needs to handle, it can overheat, leading to insulation damage, fires, or equipment failure. On the other hand, using a wire that’s too large for the application can be unnecessarily expensive and difficult to work with. Proper wire sizing ensures that your electrical system operates efficiently and safely.
Factors such as the material of the wire, the length of the run, and the type of load also play a role in determining the appropriate size. For example, a 100-amp service in a residential setting may require different wire sizes compared to a commercial application. Understanding these factors will help you make informed decisions when selecting wire for your project.
What Are the Common Wire Materials?
The two most common materials used for electrical wiring are copper and aluminum. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Copper: Highly conductive, durable, and resistant to corrosion. It’s the preferred choice for most residential and commercial applications but tends to be more expensive.
- Aluminum: Lighter and less expensive than copper, making it ideal for long-distance runs or large installations. However, it’s less conductive and requires careful handling to avoid oxidation and connection issues.
Choosing the right material depends on your budget, the specific application, and local building codes. For a 100-amp service, copper is often the safer and more reliable option, especially for shorter runs.
Read also:Czech Wife Swap Site Exploring The Culture And Community
How Far Can You Run 100 Amp Wire?
The distance you can run a 100-amp wire depends on the voltage drop, which occurs when electrical current travels through a wire. Voltage drop can reduce the efficiency of your electrical system and cause appliances to underperform. To minimize voltage drop, you may need to increase the wire size for longer runs.
For example, a 2 AWG copper wire can typically handle a 100-amp load over a distance of 100 feet without significant voltage drop. However, if the run exceeds 100 feet, you may need to upgrade to a larger gauge, such as 1/0 AWG copper or 2/0 AWG aluminum. Always calculate the voltage drop for your specific application to ensure optimal performance.
Is Copper Better Than Aluminum?
While both materials are commonly used for electrical wiring, copper is generally considered superior due to its higher conductivity and durability. Copper wires can carry the same current as aluminum with a smaller gauge, making them easier to work with and more efficient. Additionally, copper is less prone to corrosion and oxidation, which can cause connection issues with aluminum wires.
However, aluminum is still a viable option for certain applications, especially when cost is a concern. It’s important to use anti-oxidant compounds and proper connectors when working with aluminum to prevent issues. For a 100-amp service, copper is often the better choice, but aluminum can be used if installed correctly.
What Are the NEC Requirements?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides specific guidelines for wire sizing to ensure safety and compliance. For a 100-amp service, the NEC recommends using 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum wire. These recommendations are based on the wire’s ability to handle the current safely without overheating.
It’s important to note that local building codes may have additional requirements, so always check with your local authorities or a licensed electrician before starting your project. The NEC also provides tables and formulas for calculating voltage drop and wire size, which can be helpful for more complex installations.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop is an important consideration when selecting wire size, especially for long-distance runs. To calculate voltage drop, you’ll need to know the wire’s resistance, the length of the run, and the current load. The formula for voltage drop is:
Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000
For example, if you’re running a 100-amp load over 150 feet with 2 AWG copper wire, the voltage drop would be approximately 3.6 volts. This is within the acceptable range, but if the voltage drop exceeds 3% of the supply voltage, you may need to increase the wire size.
What Size Wire for 100 Amps Subpanel?
When installing a subpanel for a 100-amp service, the wire size requirements are similar to those for a main panel. For copper wire, 2 AWG is typically sufficient, while 1/0 AWG aluminum is recommended. The key difference is that subpanels often require additional considerations, such as grounding and bonding, to ensure safety.
Always use the appropriate wire size and follow NEC guidelines when installing a subpanel. If you’re unsure about the requirements, consult a licensed electrician to ensure compliance with local codes and safety standards.
What Are the Safety Tips?
Electrical wiring can be dangerous if not done correctly. Here are some safety tips to keep in mind when working with 100-amp wire:
- Always turn off the power before working on electrical systems.
- Use the correct wire size and material for your application.
- Follow NEC guidelines and local building codes.
- Use anti-oxidant compounds when working with aluminum wire.
- Consult a licensed electrician if you’re unsure about any aspect of the installation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What size wire for 100 amps is recommended for residential use?
For residential applications, 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum is typically recommended for a 100-amp service.
Can I use 4 AWG wire for 100 amps?
No, 4 AWG wire is not suitable for a 100-amp service as it cannot safely carry the required current. Always use the appropriate wire size to avoid safety hazards.
How do I know if my wire size is correct?
Check the NEC guidelines and consult a licensed electrician to ensure your wire size meets safety and code requirements.
By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can ensure that your electrical system is safe, efficient, and compliant with all relevant standards. Remember, when it comes to electrical work, safety should always be your top priority. Whether you’re a homeowner or a professional electrician, understanding what size wire for 100 amps is essential for any project involving electrical wiring.
Understanding The Right Wire Gauge For 100 Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
Is Fungi Autotrophic Or Heterotrophic? Unraveling The Mystery Of Fungal Nutrition
Discover The Magic Of Vanillagift.c9m: Your Ultimate Guide

Copper Wire For 100 Amps
What Is the Correct Wire Size for 100Amp Service? Angi