Fungi Heterotrophic: Unveiling The Secrets Of Nature's Decomposers
Fungi heterotrophic organisms play a crucial role in ecosystems worldwide, acting as nature's recyclers. These fascinating life forms rely on external sources of organic matter for nutrition, breaking down complex compounds into simpler ones. Unlike plants, fungi lack chlorophyll and cannot produce their own food through photosynthesis. Instead, they have evolved unique mechanisms to obtain nutrients, making them indispensable in maintaining ecological balance. From forests to agricultural fields, fungi heterotrophic activity ensures nutrient cycling and soil health.
Fungi heterotrophic organisms are found in diverse environments, from the deepest soils to the highest tree canopies. Their ability to decompose organic material is essential for breaking down dead plants, animals, and other organic debris. This decomposition process releases vital nutrients back into the soil, promoting plant growth and sustaining entire ecosystems. Scientists continue to study fungi heterotrophic mechanisms to better understand their role in carbon cycling and climate regulation.
The study of fungi heterotrophic behavior has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential applications in biotechnology, agriculture, and environmental conservation. Researchers are exploring how these organisms can be harnessed to degrade pollutants, improve soil fertility, and even produce sustainable biofuels. With their remarkable adaptability and resilience, fungi heterotrophic species offer promising solutions to some of the world's most pressing environmental challenges.
Read also:Who Is Erin Burnetts Spouse A Deep Dive Into Her Personal Life
- What Are Fungi Heterotrophic?
- Why Are Fungi Heterotrophic Important for Ecosystems?
- How Do Fungi Heterotrophic Obtain Nutrients?
- Can Fungi Heterotrophic Help Fight Climate Change?
- Types of Fungi Heterotrophic
- Fungi Heterotrophic in Agriculture
- How Do Fungi Heterotrophic Decompose Material?
- Fungi Heterotrophic and Biotechnology
- Fungi Heterotrophic in Our Daily Lives
- Future Research on Fungi Heterotrophic
What Are Fungi Heterotrophic?
Fungi heterotrophic organisms are a diverse group of life forms that obtain their nutrients by breaking down organic material. Unlike autotrophs, such as plants, which produce their own food through photosynthesis, fungi rely entirely on external sources for sustenance. This makes them unique among living organisms and highlights their importance in nutrient cycling. Fungi heterotrophic species can be found in almost every environment, from tropical rainforests to arid deserts, showcasing their adaptability and resilience.
Why Are Fungi Heterotrophic Important for Ecosystems?
Fungi heterotrophic organisms play a vital role in maintaining the health of ecosystems. They break down dead plants, animals, and other organic matter, returning essential nutrients to the soil. This process, known as decomposition, is crucial for sustaining plant growth and supporting food chains. Without fungi heterotrophic activity, organic waste would accumulate, and ecosystems would struggle to function effectively. Additionally, fungi contribute to carbon cycling, helping regulate atmospheric CO2 levels.
How Do Fungi Heterotrophic Obtain Nutrients?
Fungi heterotrophic organisms use specialized structures called hyphae to absorb nutrients from their surroundings. These thread-like structures secrete enzymes that break down complex organic compounds into simpler molecules, which the fungi can then absorb. This process allows fungi to thrive in environments where other organisms might struggle to survive. Fungi heterotrophic species are highly efficient decomposers, capable of breaking down tough materials like cellulose and lignin.
Can Fungi Heterotrophic Help Fight Climate Change?
Fungi heterotrophic organisms have the potential to play a significant role in combating climate change. By breaking down organic matter, they help sequester carbon in the soil, reducing the amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere. Additionally, certain fungi heterotrophic species can degrade pollutants and toxins, making them valuable tools for environmental remediation. Researchers are actively exploring these capabilities to develop sustainable solutions for mitigating climate change.
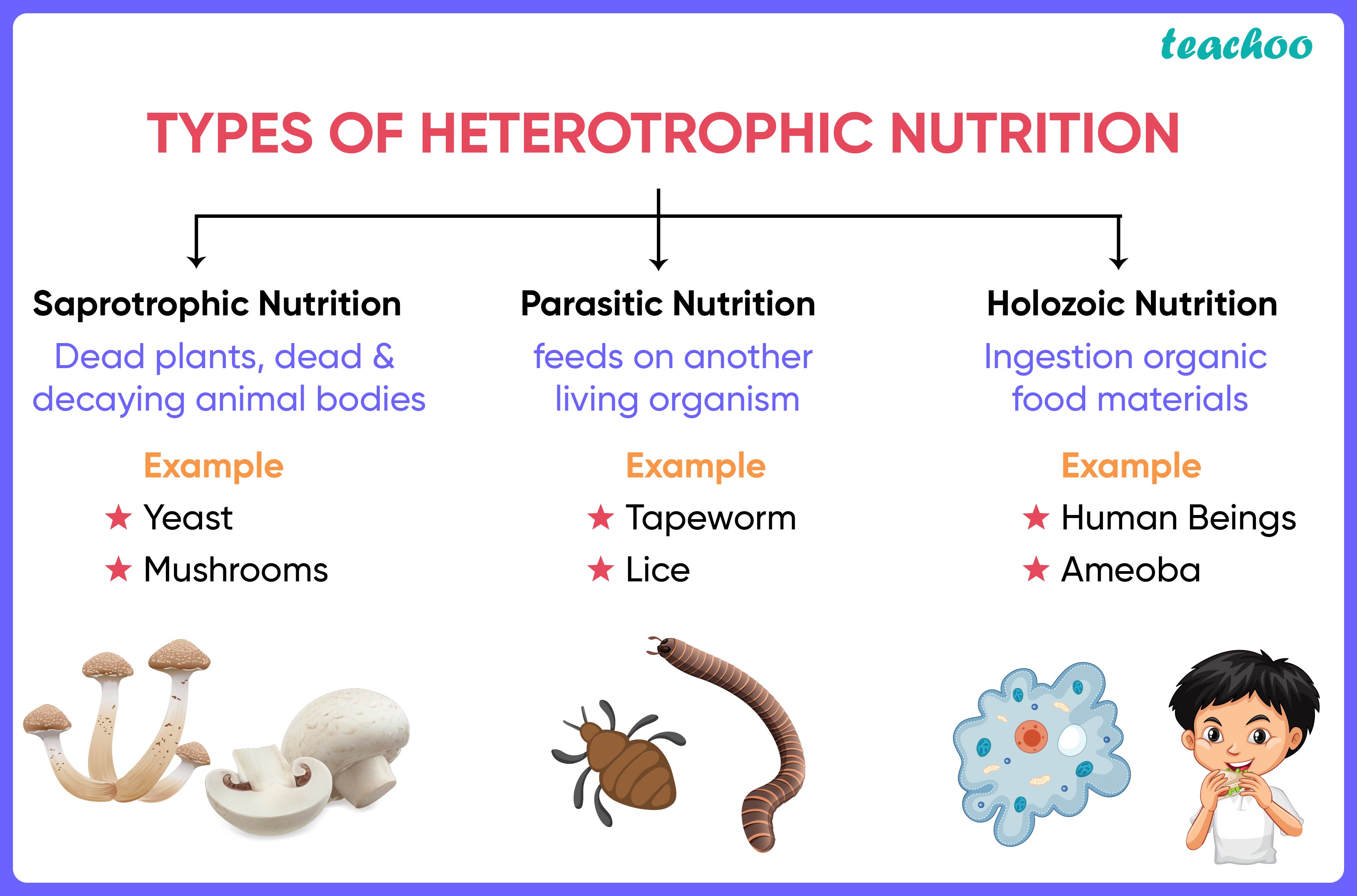
Types of Fungi Heterotrophic
There are several types of fungi heterotrophic organisms, each with unique characteristics and ecological roles. Some of the most common types include:
- Saprotrophic Fungi: These fungi decompose dead organic matter, such as fallen leaves and wood.
- Parasitic Fungi: These fungi obtain nutrients from living hosts, often causing diseases in plants and animals.
- Mycorrhizal Fungi: These fungi form symbiotic relationships with plants, helping them absorb nutrients from the soil.
- Endophytic Fungi: These fungi live inside plant tissues without causing harm, offering protection against pathogens.
Fungi Heterotrophic in Agriculture
Fungi heterotrophic species are essential for agriculture, contributing to soil fertility and plant health. Mycorrhizal fungi, for example, form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, enhancing their ability to absorb water and nutrients. This relationship improves crop yields and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers. Additionally, fungi heterotrophic organisms help control pests and diseases, making them valuable allies for sustainable farming practices.
Read also:Exploring The Legacy Of James And Scott Caan A Deep Dive Into Their Lives And Careers
How Do Fungi Heterotrophic Decompose Material?
Fungi heterotrophic organisms decompose material through a process called enzymatic digestion. They secrete enzymes that break down complex organic compounds, such as cellulose and lignin, into simpler molecules. These molecules are then absorbed by the fungi, providing them with the nutrients they need to grow and reproduce. This decomposition process is essential for recycling nutrients and maintaining soil health.
Fungi Heterotrophic and Biotechnology
Fungi heterotrophic species are increasingly being used in biotechnology for their ability to produce valuable compounds. For example, certain fungi are used to produce antibiotics, enzymes, and biofuels. Their ability to break down complex materials also makes them useful for degrading pollutants and toxins. Researchers are exploring new applications for fungi heterotrophic organisms, from developing sustainable packaging materials to creating novel medicines.
Fungi Heterotrophic in Our Daily Lives
Fungi heterotrophic organisms impact our daily lives in ways we often overlook. They are used in the production of bread, beer, and cheese, as well as in the development of life-saving medicines like penicillin. Additionally, fungi heterotrophic species play a role in waste management, breaking down organic waste in landfills and compost piles. Their versatility and adaptability make them indispensable to both nature and human society.
Future Research on Fungi Heterotrophic
The study of fungi heterotrophic organisms is an exciting and rapidly evolving field. Researchers are exploring new ways to harness their capabilities for environmental conservation, agriculture, and biotechnology. Future research could uncover novel applications for fungi heterotrophic species, from developing sustainable materials to addressing global challenges like climate change and food security. By continuing to study these remarkable organisms, we can unlock their full potential and create a more sustainable future.
In conclusion, fungi heterotrophic organisms are indispensable to life on Earth. Their ability to decompose organic matter, recycle nutrients, and support ecosystems makes them vital for maintaining the planet's health. By understanding and harnessing their unique capabilities, we can address some of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time. Whether in agriculture, biotechnology, or daily life, fungi heterotrophic species continue to inspire and amaze us with their versatility and resilience.
Does Bleach Lose Its Potency Over Time? Exploring The Facts
Choosing The Right Wire Size For A 100 Amp Service: A Complete Guide
Exploring The Fascinating World Of The Seven Sided Regular Polygon
Heterotrophic Nutrition Definition, Types, Examples Teachoo

Free clipart fungi ClipartFox Clipart Library Clipart Library Clip