Understanding 0 Celsius: The Science, Significance, And Everyday Applications
This temperature holds a unique place in thermodynamics, meteorology, and even culinary arts. Whether you're studying the freezing point of water, preparing for winter weather, or calibrating scientific instruments, 0 Celsius is a cornerstone of understanding temperature. Its role extends beyond the laboratory, influencing how we live, work, and interact with the world around us. By exploring the significance of 0 Celsius, we can better appreciate its impact on both natural phenomena and human activities.
The concept of 0 Celsius, also known as the freezing point of water, has been a fundamental reference point since the development of the Celsius scale in the 18th century. It serves as a universal standard for measuring temperature, enabling scientists, engineers, and everyday individuals to communicate and collaborate effectively. From understanding climate patterns to ensuring the safety of food storage, this temperature plays a critical role in countless applications. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it bridges the gap between theoretical science and practical utility.
In this article, we will delve into the science behind 0 Celsius, its real-world applications, and how it influences various fields. By answering common questions and providing detailed insights, we aim to equip you with a deeper understanding of this pivotal temperature. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply curious about the world around you, this exploration of 0 Celsius will offer valuable knowledge and context. Let’s begin by examining the origins and definitions of this remarkable benchmark.
Read also:Exploring The Legacy Of James Caans Son A Rising Star In Hollywood
- What is 0 Celsius?
- Why is 0 Celsius Important?
- How Does 0 Celsius Affect Water?
- Is 0 Celsius the Same as 32 Fahrenheit?
- What Are the Practical Applications of 0 Celsius?
- How Do Scientists Use 0 Celsius?
- How Does 0 Celsius Impact Weather?
- What Happens to Materials at 0 Celsius?
- Why is 0 Celsius a Key Reference Point?
- How Can You Measure 0 Celsius Accurately?
What is 0 Celsius?
0 Celsius is the temperature at which water freezes under standard atmospheric pressure. This benchmark was established by Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, in 1742 when he developed the Celsius temperature scale. The scale was designed to be intuitive, with 0 representing the freezing point of water and 100 representing its boiling point. This simplicity made the Celsius scale widely adopted across the globe, especially in scientific and educational contexts.
The freezing point of water is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical implications in various fields. For example, it is critical for understanding phase transitions, such as the transformation of liquid water into ice. This phenomenon is governed by the laws of thermodynamics and is influenced by factors like pressure and impurities in the water. At 0 Celsius, the molecular structure of water changes, leading to the formation of a crystalline lattice that we recognize as ice.
Why Does Water Freeze at 0 Celsius?
Water freezes at 0 Celsius because, at this temperature, the kinetic energy of water molecules decreases to a point where they can no longer move freely. Instead, they arrange themselves into a fixed, orderly structure. This process is reversible, meaning that when the temperature rises above 0 Celsius, the ice melts back into liquid water. Understanding this transition is essential for fields like meteorology, where predicting ice formation is crucial for weather forecasting.
Why is 0 Celsius Important?
0 Celsius is more than just a number on a thermometer; it is a cornerstone of scientific measurement and everyday life. Its importance stems from its role as a reference point for temperature scales and its influence on natural processes. For instance, the freezing point of water affects ecosystems, agriculture, and human infrastructure. Ice formation at 0 Celsius can lead to frost, snow, and other weather phenomena that shape our environment.
How Does 0 Celsius Affect Water?
At 0 Celsius, water undergoes a phase change that has far-reaching consequences. When water freezes, it expands, which is why ice floats on liquid water. This property is vital for aquatic life, as it creates an insulating layer of ice on the surface of lakes and rivers, protecting the organisms below from freezing temperatures. Additionally, the expansion of water at 0 Celsius can cause damage to pipes and other structures, highlighting the need for proper insulation in cold climates.
Is 0 Celsius the Same as 32 Fahrenheit?
Yes, 0 Celsius is equivalent to 32 Fahrenheit. This equivalence is a result of the mathematical relationship between the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. While the Celsius scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, the Fahrenheit scale uses a different reference point, with 32 degrees representing the freezing point of water. Understanding this conversion is essential for anyone working with temperature data, especially in international contexts.
Read also:Strongexploring The Intriguing World Of Czechwife Swap 12 A Comprehensive Guidestrong
Why Do We Use Different Temperature Scales?
Different temperature scales exist because they were developed independently to meet specific needs. For example, the Fahrenheit scale was created by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century and was widely used in English-speaking countries until the adoption of the Celsius scale. Today, the Celsius scale is preferred in scientific and international contexts due to its simplicity and alignment with the metric system.
What Are the Practical Applications of 0 Celsius?
0 Celsius has numerous practical applications across various fields. In meteorology, it is used to predict weather patterns, such as frost and snowfall. In the food industry, it is essential for preserving perishable goods, as refrigeration systems are often calibrated to maintain temperatures just above 0 Celsius. Additionally, 0 Celsius is a critical reference point for calibrating thermometers and other temperature-measuring devices.
How Do Scientists Use 0 Celsius?
Scientists rely on 0 Celsius as a standard for experiments and measurements. For example, it is used in chemistry to determine the melting and freezing points of substances. In physics, it serves as a baseline for studying thermodynamic processes. Researchers also use 0 Celsius to study the behavior of materials under different temperature conditions, such as the conductivity of metals or the viscosity of liquids.
How Does 0 Celsius Impact Weather?
At 0 Celsius, water vapor in the atmosphere can condense and freeze, leading to the formation of frost, snow, and ice. These phenomena have significant implications for weather patterns and human activities. For instance, frost can damage crops, while snow and ice can disrupt transportation and communication systems. Understanding the role of 0 Celsius in weather helps meteorologists make accurate predictions and issue timely warnings.
What Happens to Materials at 0 Celsius?
At 0 Celsius, materials may undergo changes in their physical properties. For example, metals may contract, and liquids may become more viscous. These changes can affect the performance of machinery and equipment, especially in cold climates. Engineers must account for these effects when designing systems that operate in environments where temperatures approach 0 Celsius.
Why is 0 Celsius a Key Reference Point?
0 Celsius serves as a universal reference point for temperature measurement, enabling consistency and accuracy across different fields. Its use as the freezing point of water provides a tangible and relatable benchmark for understanding temperature. This standardization is crucial for scientific research, industrial processes, and everyday applications, ensuring that temperature data is reliable and comparable worldwide.
How Can You Measure 0 Celsius Accurately?
To measure 0 Celsius accurately, you need a calibrated thermometer and a controlled environment. Digital thermometers are often preferred for their precision, but traditional mercury or alcohol thermometers can also be used. It is essential to ensure that the thermometer is properly calibrated and that external factors, such as pressure and humidity, do not affect the reading. By following these steps, you can obtain accurate measurements of 0 Celsius for various applications.
In conclusion, 0 Celsius is a temperature that holds immense significance in science, industry, and daily life. Its role as the freezing point of water makes it a critical reference point for understanding natural phenomena and developing practical solutions. By exploring its applications and implications, we can appreciate the profound impact of this seemingly simple temperature. Whether you're studying the properties of water, predicting weather patterns, or calibrating instruments, 0 Celsius remains an indispensable benchmark in our understanding of the world.
Understanding Half Of 1 1/3 Cups: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring The World Of ㅍ무ㅑㅣㅣㅁ햜.채ㅡ: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Autotrophic And Heterotrophic Life: A Comprehensive Guide
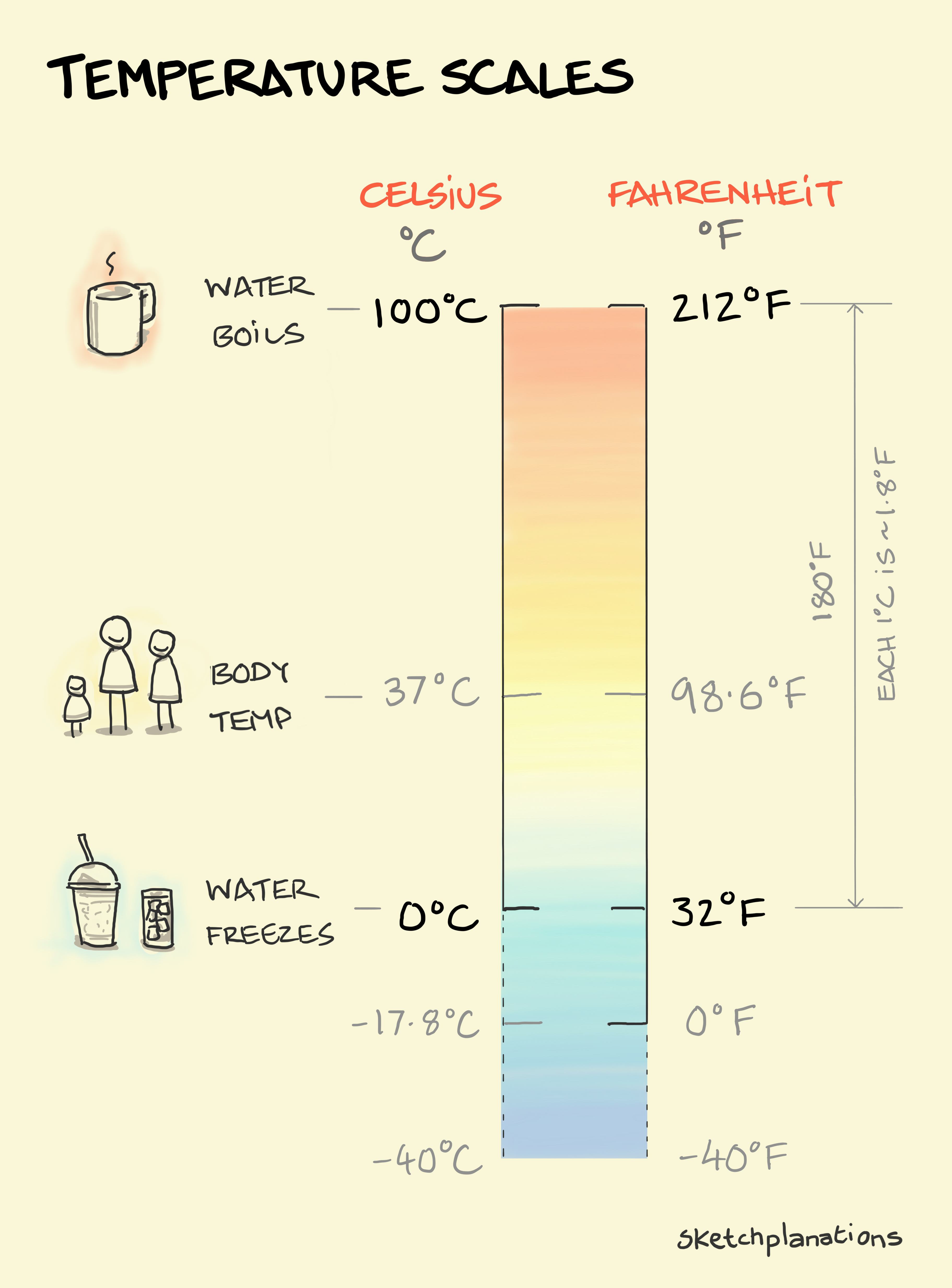
Fahrenheit and Celsius Sketchplanations

How to Convert Celsius to Kelvin 10 Steps (with Pictures)