How Fast Is The Voyager 1 Spacecraft Traveling? Exploring The Speed Of Humanity's Farthest Space Probe
How fast is the Voyager 1 spacecraft traveling? This question has intrigued space enthusiasts and scientists alike for decades. Launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, Voyager 1 has become the farthest human-made object from Earth, venturing into the vast unknown of interstellar space. It travels at an incredible speed, carrying humanity's hopes, dreams, and scientific curiosity across billions of miles. This spacecraft continues to send valuable data back to Earth, even after more than four decades of operation.
Voyager 1's speed is not just a number; it represents the pinnacle of human engineering and exploration. The spacecraft moves at approximately 38,000 miles per hour (61,000 kilometers per hour), making it one of the fastest objects ever created by humans. This velocity has allowed it to escape the gravitational pull of our solar system and enter interstellar space in 2012. Understanding its speed gives us insight into the capabilities of space exploration technology and the challenges of navigating the cosmos.
As Voyager 1 continues its journey, it raises fascinating questions about the limits of human knowledge and the potential for future space missions. How fast is the Voyager 1 spacecraft traveling? Why is its speed significant? What can we learn from its ongoing mission? These questions not only deepen our understanding of space exploration but also inspire future generations to push the boundaries of what is possible.
Read also:Greg Gutfeld And Wife A Closer Look At Their Life Together
- What Is the Speed of Voyager 1?
- How Does Voyager 1's Speed Compare to Other Spacecraft?
- Why Is the Speed of Voyager 1 Significant?
- How Fast Is the Voyager 1 Spacecraft Traveling, and What Does It Mean for Space Exploration?
- What Are the Challenges of Maintaining Speed in Space?
- How Does Voyager 1 Communicate with Earth?
- What Can We Learn from Voyager 1's Speed?
- How Fast Is the Voyager 1 Spacecraft Traveling in Comparison to Light Speed?
- What Is the Future of Voyager 1?
- Conclusion: The Legacy of Voyager 1
What Is the Speed of Voyager 1?
Voyager 1 travels at an impressive speed of approximately 38,000 miles per hour (61,000 kilometers per hour). This velocity is crucial for its mission, as it allows the spacecraft to overcome the gravitational forces of the Sun and other celestial bodies. The speed of Voyager 1 was achieved through a combination of its initial launch velocity and gravitational assists from planets like Jupiter and Saturn.
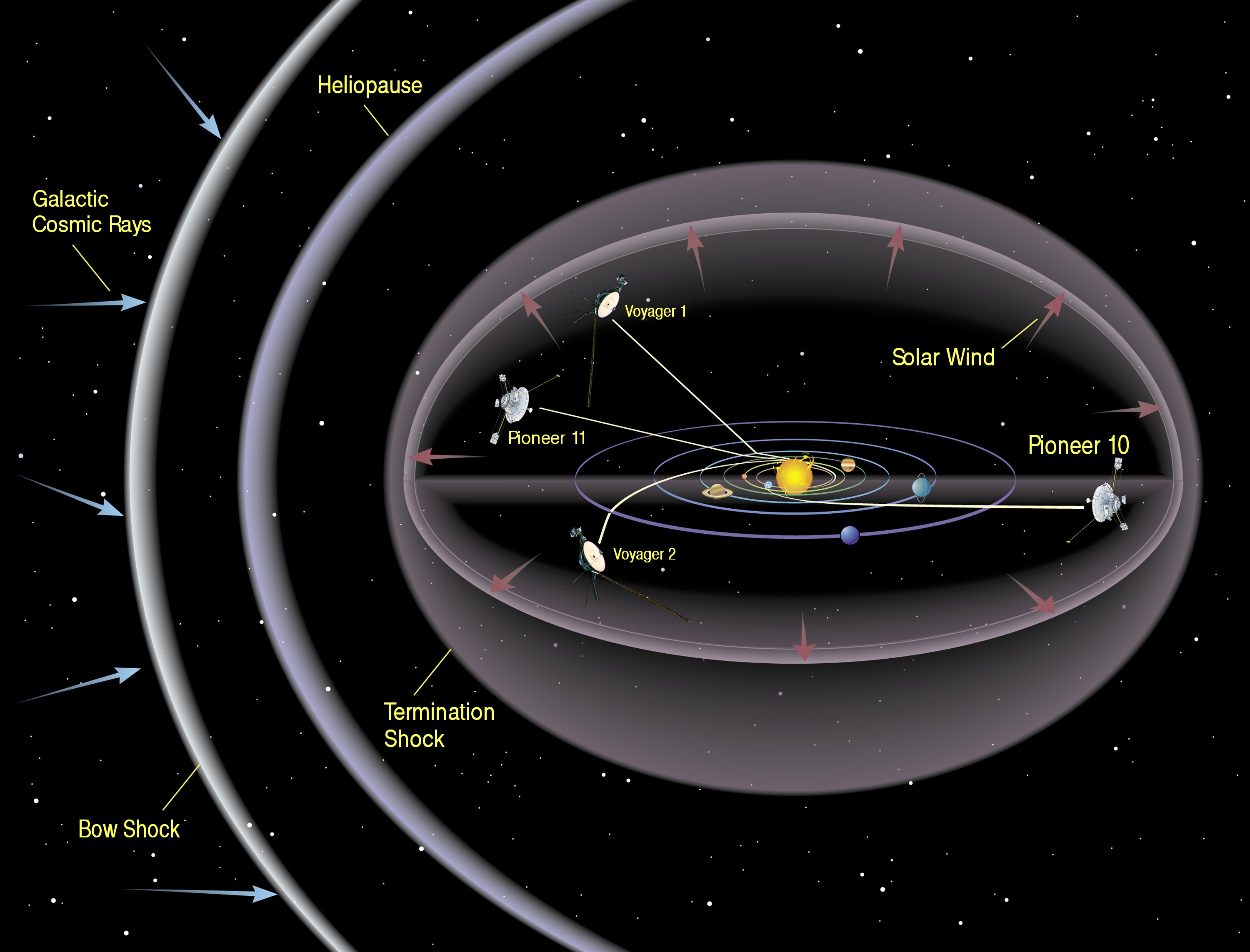
Gravitational assists, also known as slingshot maneuvers, involve using the gravity of a planet to increase the spacecraft's speed. This technique was instrumental in propelling Voyager 1 to its current velocity. Without these maneuvers, the spacecraft would not have been able to reach its current position beyond the heliosphere, the boundary of our solar system.
Understanding the speed of Voyager 1 is essential for appreciating its achievements. It has traveled more than 14 billion miles (22.5 billion kilometers) from Earth, a distance that would take light over 21 hours to cover. This makes Voyager 1 not only one of the fastest spacecraft but also one of the most distant.
How Does Voyager 1's Speed Compare to Other Spacecraft?
When comparing Voyager 1's speed to other spacecraft, it stands out as one of the fastest. For example, the New Horizons spacecraft, which visited Pluto in 2015, reached speeds of up to 36,000 miles per hour (58,000 kilometers per hour) during its journey. While slightly slower than Voyager 1, New Horizons achieved its velocity through a powerful launch and minimal gravitational assists.
Another notable comparison is with the Parker Solar Probe, which holds the record for the fastest human-made object. The Parker Solar Probe reaches speeds of over 430,000 miles per hour (700,000 kilometers per hour) as it orbits the Sun. However, this speed is achieved in the intense gravitational field of the Sun, making it an entirely different context from Voyager 1's journey through interstellar space.
Voyager 1's sustained speed over decades is what makes it unique. While other spacecraft may achieve higher velocities for short periods, Voyager 1's ability to maintain its speed in the vast emptiness of space is a testament to its design and engineering.
Read also:Couple Swap Czech Exploring Relationships And Lifestyle Choices
Why Is the Speed of Voyager 1 Significant?
The speed of Voyager 1 is significant for several reasons. First, it represents the culmination of decades of scientific and engineering advancements. The spacecraft's ability to travel at such high speeds while maintaining communication with Earth is a remarkable achievement in space exploration.
Second, Voyager 1's speed allows it to explore regions of space that were previously inaccessible. By traveling beyond the heliosphere, it has provided scientists with invaluable data about interstellar space, including the density of plasma and the presence of cosmic rays. This information helps us understand the environment outside our solar system and the potential for future interstellar missions.
Finally, the speed of Voyager 1 serves as a benchmark for future spacecraft. As humanity looks toward exploring other star systems, understanding how to achieve and maintain high velocities in space is crucial. Voyager 1's journey provides a foundation for developing new technologies and strategies for long-distance space travel.
How Fast Is the Voyager 1 Spacecraft Traveling, and What Does It Mean for Space Exploration?
How fast is the Voyager 1 spacecraft traveling? At approximately 38,000 miles per hour (61,000 kilometers per hour), Voyager 1 is paving the way for future space exploration missions. Its journey demonstrates the potential for long-term missions that can gather data from distant regions of the universe.
The spacecraft's speed has allowed it to escape the gravitational pull of the Sun and enter interstellar space, a feat that was once thought impossible. By studying the conditions in interstellar space, scientists can better understand the boundaries of our solar system and the nature of the universe beyond.
Voyager 1's speed also highlights the importance of sustainability in space missions. The spacecraft has been operational for over 40 years, relying on its initial velocity and minimal energy consumption to continue its mission. This serves as a model for designing future spacecraft that can operate efficiently over long periods.
What Are the Challenges of Maintaining Speed in Space?
Maintaining speed in space presents numerous challenges, even for a spacecraft as advanced as Voyager 1. One of the primary challenges is the lack of friction in space. Unlike on Earth, where friction can slow down moving objects, space is a vacuum, meaning there is no resistance to slow the spacecraft down.
Another challenge is the limited energy supply. Voyager 1 relies on radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) for power, which convert heat from decaying plutonium into electricity. As the plutonium decays, the power output decreases, requiring careful management of the spacecraft's systems to conserve energy.
Despite these challenges, Voyager 1 has managed to maintain its speed and continue its mission. This is a testament to the ingenuity of its designers and the robustness of its systems. Understanding these challenges provides valuable insights into the design of future spacecraft capable of long-duration missions.
How Does Voyager 1 Communicate with Earth?
Voyager 1 communicates with Earth using a high-gain antenna that transmits data at a frequency of 2.3 GHz. The spacecraft's signals take over 21 hours to reach Earth due to the vast distance between them. Despite this delay, scientists are able to receive valuable data about interstellar space.
The communication system on Voyager 1 is designed to operate with minimal power, ensuring that it can continue sending data even as its energy supply diminishes. This system has been critical for maintaining contact with the spacecraft over the decades.
How fast is the Voyager 1 spacecraft traveling? Its speed plays a role in communication as well. As the spacecraft moves farther away from Earth, the signal strength decreases, requiring sophisticated technology to decode the transmitted data. This highlights the importance of advanced communication systems in space exploration.
What Can We Learn from Voyager 1's Speed?
Voyager 1's speed offers valuable lessons for future space missions. One key takeaway is the importance of gravitational assists in achieving high velocities. By leveraging the gravity of planets, spacecraft can gain significant speed without expending additional fuel.
Another lesson is the need for sustainable design. Voyager 1's ability to maintain its speed and continue its mission for over 40 years demonstrates the importance of building spacecraft that can operate efficiently over long periods. This is particularly relevant as humanity looks toward exploring other star systems.
Finally, Voyager 1's speed highlights the potential for long-distance space exploration. By traveling billions of miles from Earth, it has shown that humanity is capable of reaching far beyond our solar system. This inspires future generations to dream big and push the boundaries of what is possible.
How Fast Is the Voyager 1 Spacecraft Traveling in Comparison to Light Speed?
While Voyager 1 travels at an impressive 38,000 miles per hour (61,000 kilometers per hour), its speed is minuscule compared to the speed of light. Light travels at approximately 186,000 miles per second (300,000 kilometers per second), making it over 20,000 times faster than Voyager 1.
This comparison underscores the vast distances involved in space exploration. Even at its incredible speed, it would take Voyager 1 tens of thousands of years to reach the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, which is located over 4 light-years away. This highlights the challenges of interstellar travel and the need for new technologies to achieve faster speeds.
How fast is the Voyager 1 spacecraft traveling? While its speed is remarkable by human standards, it serves as a reminder of the immense scale of the universe and the limitations of current space travel technology.
What Is the Future of Voyager 1?
The future of Voyager 1 is uncertain but promising. As its power supply continues to diminish, scientists predict that the spacecraft will lose the ability to transmit data by the mid-2020s. However, its journey will not end there.
Voyager 1 will continue traveling through interstellar space, carrying the Golden Record, a time capsule of human culture and knowledge. This record includes sounds, images, and messages intended to communicate the story of humanity to any extraterrestrial civilizations that may encounter the spacecraft.
Even after it ceases communication with Earth, Voyager 1 will remain a symbol of human curiosity and exploration. Its speed and distance from Earth will continue to inspire future generations to explore the cosmos and seek answers to the mysteries of the universe.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Voyager 1
Voyager 1's journey is a testament to human ingenuity and the desire to explore the unknown. Its speed, achieved through decades of scientific and engineering advancements, has allowed it to venture farther than any other spacecraft. How fast is the Voyager 1 spacecraft traveling? At 38,000 miles per hour (61,000 kilometers per hour), it continues to inspire awe and curiosity about the universe.
The legacy of Voyager 1 extends beyond its speed. It represents humanity's ability to overcome
How Fast Is The Voyager 1 Spacecraft Traveling? Exploring The Speed Of Humanity's Farthest Space Probe
Frog On Unicycle: The Ultimate Guide To This Quirky And Fascinating Combination
Morning In Polish: A Complete Guide To Understanding And Embracing The Beauty Of Polish Mornings
Where is voyager 1 spacecraft

Voyager 1 Spacecraft 'Has Left Solar System' Science, Climate & Tech