Is Fungi Heterotrophic? Unveiling The Secrets Of Fungal Nutrition
Are you curious about the nutritional habits of fungi and whether they are truly heterotrophic? Fungi play a vital role in ecosystems, acting as decomposers, symbionts, and even pathogens. But what exactly makes fungi heterotrophic, and why does it matter? In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of fungi, focusing on their unique nutritional strategies and answering key questions like “Is fungi heterotrophic?” By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how fungi obtain their nutrients and why this characteristic is crucial to their survival.
Fungi are often misunderstood organisms, often mistaken for plants due to their stationary nature. However, unlike plants, fungi do not photosynthesize or produce their own food. Instead, they rely on external sources of organic material to meet their nutritional needs. This dependency on organic matter is what classifies fungi as heterotrophic organisms. Understanding this fundamental aspect of fungi can deepen your appreciation for their role in nature and their importance in human life, from food production to medicine.
As we dive deeper into the topic, you’ll discover the mechanisms fungi use to break down organic matter, the differences between fungi and other heterotrophic organisms, and the implications of their heterotrophic nature on ecosystems. Whether you’re a biology enthusiast, a student, or just someone with a curious mind, this article will provide valuable insights into the world of fungi and their unique way of life. Let’s begin our exploration of the question: Is fungi heterotrophic?
Read also:Daniel Radcliffe Age 2000 A Journey Through Time And Stardom
Table of Contents
- What Does Heterotrophic Mean?
- Is Fungi Heterotrophic? How Do They Obtain Nutrients?
- Why Are Fungi Classified as Heterotrophs?
- How Do Fungi Differ from Plants?
- What Are the Types of Fungal Nutrition?
- Can Fungi Be Both Parasitic and Symbiotic?
- Why Is Fungi Heterotrophic Important for Ecosystems?
- How Do Fungi Decompose Organic Matter?
- What Are the Economic Impacts of Fungi?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Fungi
What Does Heterotrophic Mean?
Heterotrophic organisms are those that cannot produce their own food and must rely on external sources of organic material to meet their energy and nutrient needs. This contrasts with autotrophic organisms, such as plants, which can produce their own food through processes like photosynthesis. Heterotrophs include animals, fungi, and many types of bacteria. They obtain nutrients by consuming other organisms or organic matter, breaking it down into simpler compounds that can be absorbed and utilized.
Is Fungi Heterotrophic? How Do They Obtain Nutrients?
Fungi are indeed heterotrophic, as they lack the ability to photosynthesize or produce their own food. Instead, they secrete enzymes onto their food source, breaking it down into simpler molecules that can be absorbed through their cell walls. This process, known as external digestion, allows fungi to thrive in diverse environments, from soil to decaying organic matter. The question “Is fungi heterotrophic?” is answered by their reliance on organic material for survival.
Why Are Fungi Classified as Heterotrophs?
Fungi are classified as heterotrophs because they cannot synthesize their own food. Unlike plants, fungi lack chlorophyll, the pigment necessary for photosynthesis. Instead, they absorb nutrients from their surroundings, making them dependent on external organic sources. This characteristic is a defining feature of fungi and sets them apart from autotrophic organisms.
How Do Fungi Differ from Plants?
Fungi and plants may appear similar due to their stationary nature, but they differ significantly in their nutritional strategies. Plants are autotrophic, producing their own food through photosynthesis, while fungi are heterotrophic, relying on organic matter for sustenance. Additionally, fungi have chitin in their cell walls, whereas plants have cellulose. These differences highlight the unique nature of fungi and answer the question: Is fungi heterotrophic?
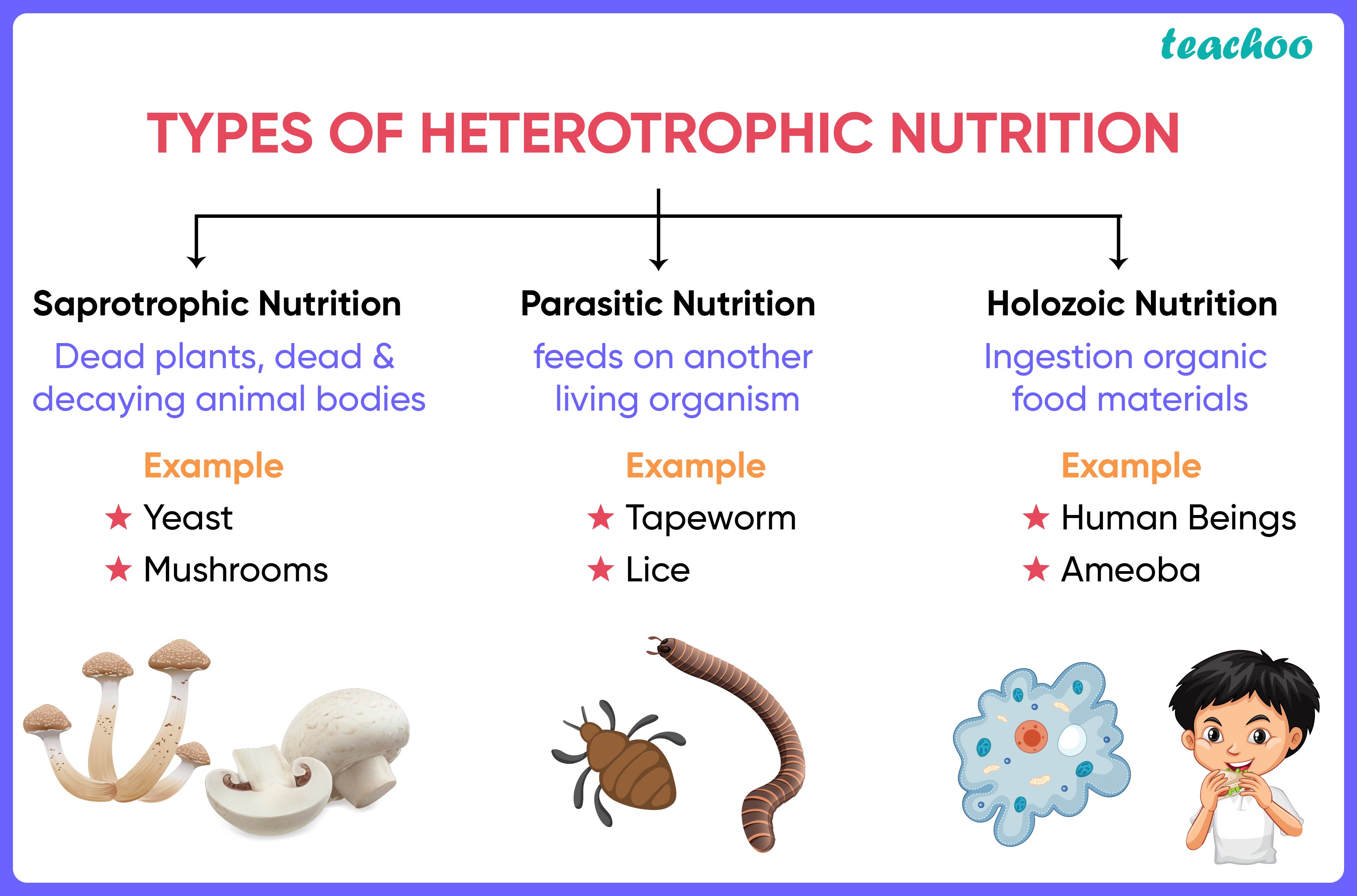
What Are the Types of Fungal Nutrition?
Fungi exhibit various nutritional strategies, including saprotrophy, parasitism, and mutualism. Saprotrophic fungi decompose dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. Parasitic fungi derive nutrients from living hosts, often causing harm. Mutualistic fungi, such as mycorrhizae, form symbiotic relationships with plants, benefiting both organisms. These strategies underscore the adaptability of fungi and their heterotrophic nature.
Can Fungi Be Both Parasitic and Symbiotic?
Yes, fungi can exhibit both parasitic and symbiotic behaviors depending on the species and environmental conditions. For example, some fungi may parasitize a host plant under certain conditions but form mutualistic relationships with other plants in different scenarios. This versatility highlights the complexity of fungal interactions and reinforces the idea that fungi are heterotrophic organisms with diverse nutritional strategies.
Read also:Does Hwang In Yeop Have A Wife Unveiling The Truth About The Rising Star
Why Is Fungi Heterotrophic Important for Ecosystems?
The heterotrophic nature of fungi is crucial for maintaining ecosystem balance. As decomposers, fungi break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus back into the soil. This process supports plant growth and contributes to the overall health of ecosystems. Without fungi, organic waste would accumulate, disrupting nutrient cycles and harming the environment.
How Do Fungi Decompose Organic Matter?
Fungi decompose organic matter through a process called external digestion. They secrete enzymes onto their food source, breaking down complex molecules like cellulose and lignin into simpler compounds. These compounds are then absorbed through the fungal cell wall, providing the nutrients fungi need to grow and reproduce. This ability to decompose organic matter is a hallmark of their heterotrophic nature.
What Are the Economic Impacts of Fungi?
Fungi have significant economic impacts, both positive and negative. On the positive side, fungi are used in food production (e.g., yeast in bread and beer), medicine (e.g., antibiotics like penicillin), and bioremediation. On the negative side, fungi can cause diseases in plants, animals, and humans, leading to economic losses. Understanding fungi’s heterotrophic nature helps us harness their benefits while mitigating their risks.
Frequently Asked Questions About Fungi
- Is fungi heterotrophic? Yes, fungi are heterotrophic organisms that rely on external organic material for nutrition.
- How do fungi obtain nutrients? Fungi obtain nutrients through external digestion, breaking down organic matter into simpler compounds.
- What is the role of fungi in ecosystems? Fungi act as decomposers, recycling nutrients and maintaining ecosystem balance.
- Can fungi be beneficial to humans? Yes, fungi are used in food production, medicine, and bioremediation, among other applications.
In conclusion, fungi are fascinating organisms whose heterotrophic nature plays a vital role in ecosystems and human life. By answering questions like “Is fungi heterotrophic?” and exploring their unique nutritional strategies, we gain a deeper appreciation for these often-overlooked organisms. Whether you’re studying biology or simply curious about the natural world, understanding fungi’s heterotrophic nature can provide valuable insights into the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
Unlocking The Power Of The Ocean: Exploring The Benefits Of Wave Energy
Understanding The Vital Role Of Cell Membrane Function In An Animal Cell
Synonyms For Effectively Communicate: Unlocking Better Connections
Heterotrophic Nutrition Definition, Types, Examples Teachoo

Free clipart fungi ClipartFox Clipart Library Clipart Library Clip