Understanding The Vital Role Of The Cell Membrane In Animal Cells
The cell membrane is one of the most critical components of an animal cell, playing an essential role in maintaining the cell's structure and functionality. Often referred to as the "gatekeeper" of the cell, the cell membrane ensures that only necessary substances enter and exit the cell while keeping harmful materials out. This selective permeability is vital for the survival and proper functioning of animal cells. Understanding the animal cell function of the cell membrane is crucial for anyone studying biology, as it forms the foundation of cellular processes and interactions.
Every living organism depends on the efficient functioning of its cells, and the cell membrane is at the heart of this process. In animal cells, the membrane is composed of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins that regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell. This dynamic structure not only protects the cell but also facilitates communication with its environment, enabling processes like nutrient absorption, waste removal, and signal transmission. By exploring the intricacies of the animal cell function of the cell membrane, we can better appreciate how cells maintain homeostasis and contribute to the overall health of an organism.
From maintaining cellular balance to enabling communication with neighboring cells, the animal cell function of the cell membrane is a topic of immense importance. Scientists and researchers have long studied this structure to understand how it contributes to cellular health and disease prevention. Whether you're a student, educator, or simply curious about biology, delving into the role of the cell membrane in animal cells can provide valuable insights into the fundamental processes that sustain life. Let’s explore this fascinating topic in greater detail.
Read also:Zack Edey Height Unveiling The Towering Presence Of A Basketball Star
- What is the Cell Membrane?
- What Are the Primary Functions of the Cell Membrane in Animal Cells?
- How Does the Cell Membrane Maintain Homeostasis?
- What Role Does the Cell Membrane Play in Cell Communication?
- Animal Cell Function of Cell Membrane in Nutrient Transport
- How Does the Cell Membrane Protect the Cell?
- Animal Cell Function of Cell Membrane in Waste Removal
- Can Damage to the Cell Membrane Affect Cell Function?
- Animal Cell Function of Cell Membrane in Medical Research
- Why Is the Cell Membrane Essential for Life?
What is the Cell Membrane?
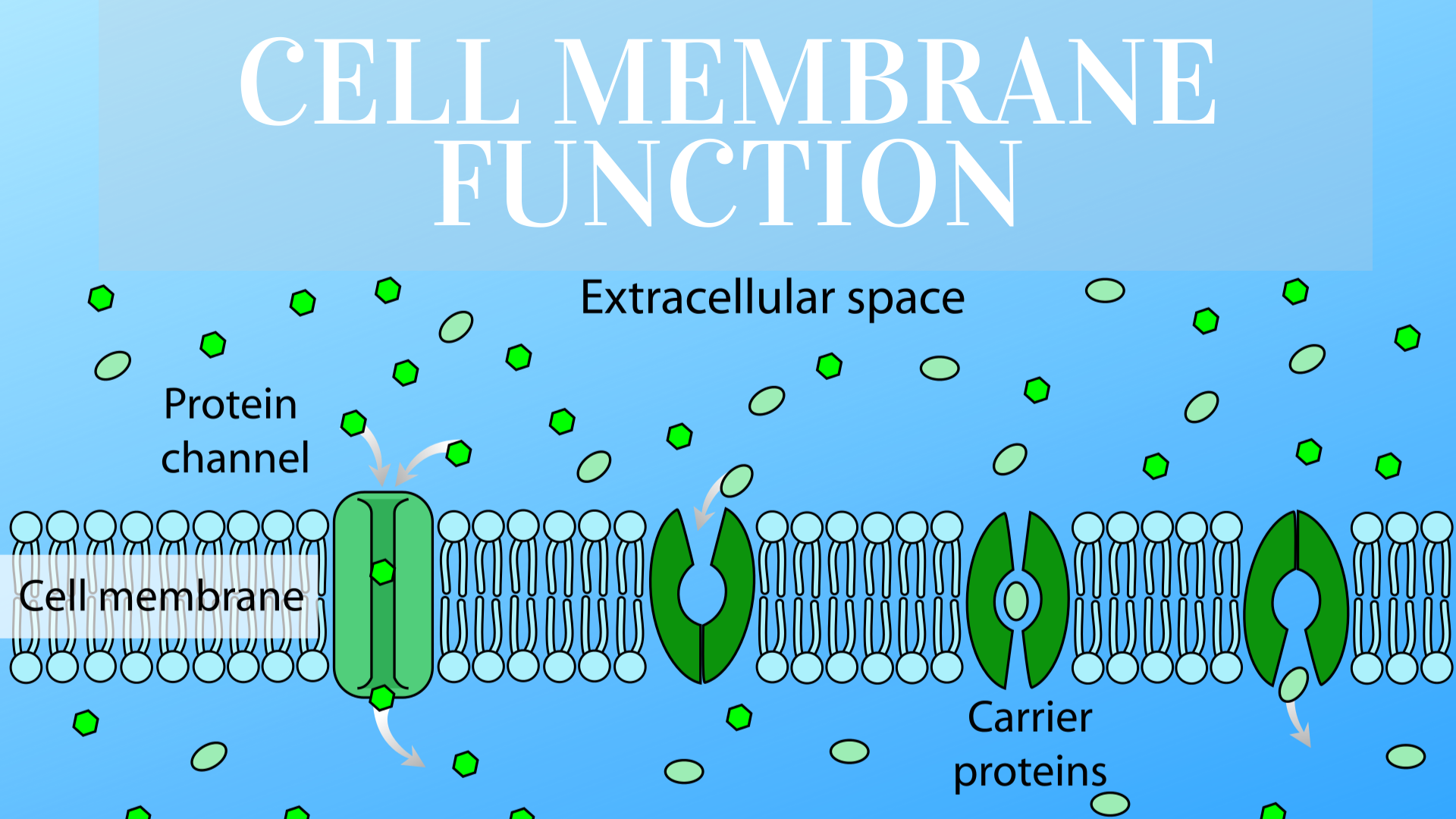
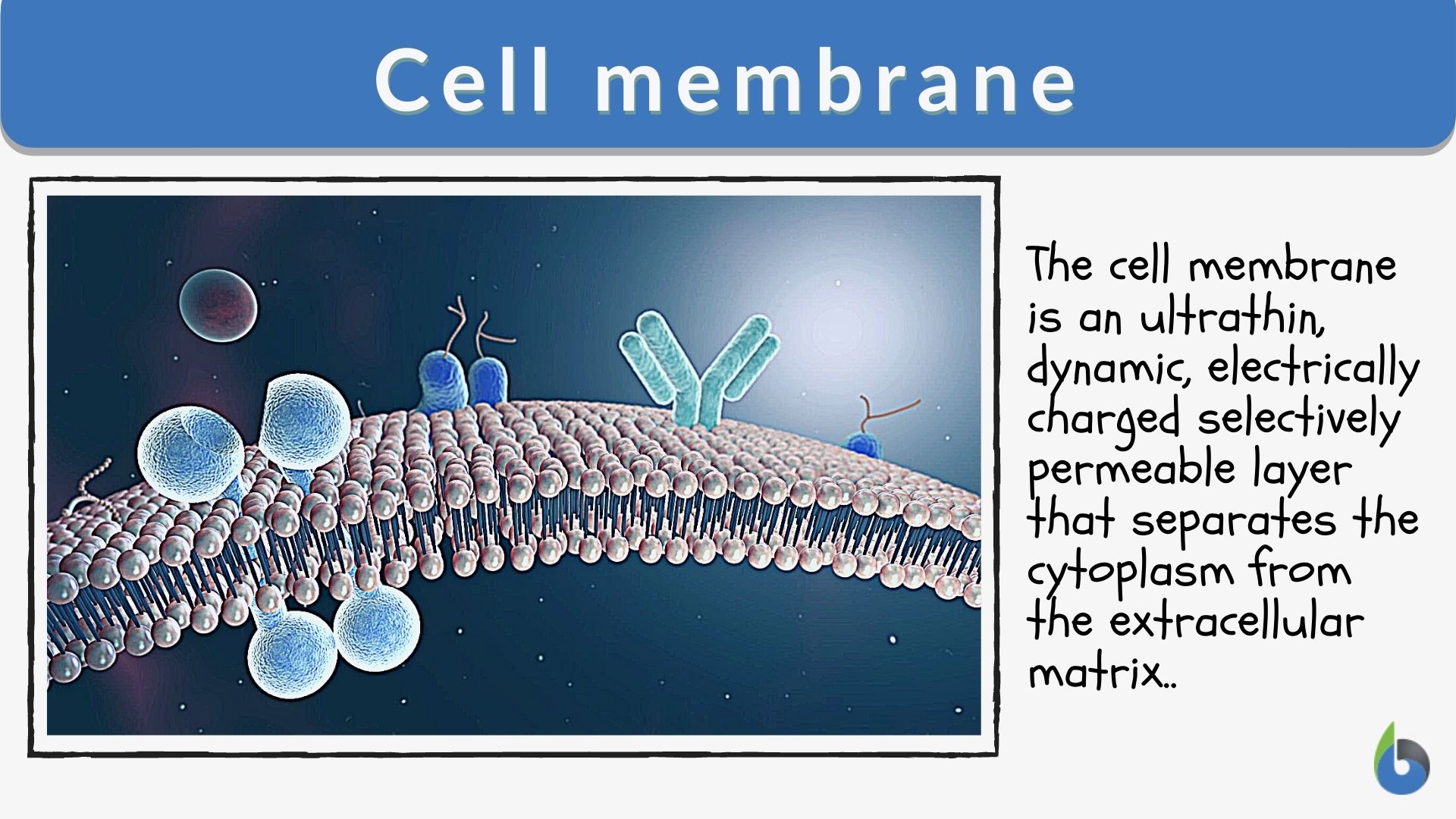
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cytoplasm of an animal cell. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. This structure gives the membrane its unique properties, such as fluidity and selective permeability. The lipid bilayer forms the foundation of the membrane, with hydrophilic (water-attracting) heads facing outward and hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails facing inward. This arrangement allows the membrane to regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell effectively.
Embedded proteins within the cell membrane serve various functions, including transporting molecules, acting as receptors for signals, and providing structural support. These proteins are crucial for the animal cell function of the cell membrane, as they enable the cell to interact with its environment. Cholesterol molecules are also present in the membrane, helping to stabilize it and maintain its fluidity under different temperature conditions. Together, these components create a dynamic and adaptable structure that is essential for cellular survival.
What Are the Primary Functions of the Cell Membrane in Animal Cells?
The primary functions of the cell membrane in animal cells are diverse and critical for maintaining cellular health. One of the most important roles is regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell. This selective permeability ensures that essential nutrients, such as glucose and ions, can enter the cell while preventing harmful substances from gaining access. The animal cell function of the cell membrane is also evident in its ability to maintain the cell's internal environment, a process known as homeostasis.
Another key function of the cell membrane is facilitating communication between cells. Specialized proteins embedded in the membrane act as receptors, allowing the cell to respond to external signals. This communication is vital for processes like immune responses, tissue repair, and hormonal regulation. Additionally, the membrane plays a role in cell recognition, enabling cells to identify each other and form tissues. These functions highlight the importance of the animal cell function of the cell membrane in maintaining the overall health and functionality of an organism.
How Does the Cell Membrane Maintain Homeostasis?
Homeostasis is the process by which cells maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in their external surroundings. The cell membrane is central to this process, as it controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. For example, it allows ions like sodium and potassium to move across the membrane through specialized channels, maintaining the cell's electrochemical balance. This regulation is a key aspect of the animal cell function of the cell membrane.
In addition to regulating ion movement, the cell membrane also helps maintain the cell's pH and osmotic balance. By controlling the flow of water and solutes, the membrane prevents the cell from swelling or shrinking excessively. This balance is crucial for the proper functioning of enzymes and other cellular processes. Through these mechanisms, the cell membrane ensures that the internal environment remains stable, enabling the cell to perform its functions efficiently.
Read also:Czech Wife Swap Site Exploring The Culture And Community
What Role Does the Cell Membrane Play in Cell Communication?
Cell communication is essential for coordinating the activities of cells within an organism. The cell membrane plays a vital role in this process by housing receptors that detect external signals, such as hormones and neurotransmitters. When a signal binds to its receptor on the membrane, it triggers a cascade of intracellular events that lead to a specific cellular response. This ability to transmit and respond to signals is a key aspect of the animal cell function of the cell membrane.
Another important aspect of cell communication is cell recognition. The membrane contains glycoproteins and glycolipids that serve as markers, allowing cells to identify each other. This recognition is crucial for processes like immune responses, where white blood cells must distinguish between self and non-self cells. By facilitating communication and recognition, the cell membrane ensures that cells can work together harmoniously to maintain the health of the organism.
Animal Cell Function of Cell Membrane in Nutrient Transport
The transport of nutrients into the cell is one of the most vital functions of the cell membrane. This process involves both passive and active transport mechanisms, each tailored to the specific needs of the cell. Passive transport, such as diffusion and osmosis, allows substances to move across the membrane without the use of energy. For example, oxygen and carbon dioxide can diffuse freely through the lipid bilayer, ensuring that the cell receives the oxygen it needs for respiration.
Active transport, on the other hand, requires energy in the form of ATP to move substances against their concentration gradient. This process is essential for transporting ions like sodium and potassium, which are critical for maintaining the cell's electrochemical balance. Specialized proteins, such as pumps and carriers, facilitate this transport. These mechanisms highlight the importance of the animal cell function of the cell membrane in ensuring that the cell receives the nutrients it needs to survive and thrive.
How Does the Cell Membrane Protect the Cell?
Protection is one of the fundamental roles of the cell membrane. By acting as a physical barrier, the membrane shields the cell from harmful substances and pathogens in its environment. This protective function is particularly important in animal cells, which lack a rigid cell wall like plant cells. The animal cell function of the cell membrane is evident in its ability to prevent the entry of toxins and other harmful molecules while allowing essential substances to pass through.
In addition to physical protection, the cell membrane also plays a role in immune defense. Specialized proteins on the membrane can recognize and bind to pathogens, triggering an immune response. This ability to detect and respond to threats is crucial for maintaining the health of the organism. By providing both physical and immunological protection, the cell membrane ensures that the cell remains safe and functional.
Animal Cell Function of Cell Membrane in Waste Removal
Removing waste products is another critical function of the cell membrane. Metabolic processes within the cell produce waste materials, such as carbon dioxide and urea, which must be expelled to prevent toxicity. The cell membrane facilitates this process by allowing waste products to diffuse out of the cell. For example, carbon dioxide, a byproduct of cellular respiration, diffuses out of the cell and into the bloodstream, where it is transported to the lungs for exhalation.
In some cases, waste removal involves active transport mechanisms. For instance, the sodium-potassium pump not only helps maintain the cell's electrochemical balance but also aids in the removal of excess sodium ions. These processes demonstrate the importance of the animal cell function of the cell membrane in maintaining a clean and healthy internal environment for the cell.
Can Damage to the Cell Membrane Affect Cell Function?
Damage to the cell membrane can have severe consequences for cell function. Since the membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell, any disruption to its structure can compromise its ability to maintain homeostasis. For example, a breach in the membrane can allow harmful substances to enter the cell, leading to cellular damage or death. This highlights the critical role of the animal cell function of the cell membrane in protecting the cell.
Moreover, damage to the membrane can impair its ability to facilitate communication and transport. For instance, if receptor proteins are damaged, the cell may fail to respond to external signals, disrupting processes like immune responses and tissue repair. Understanding the potential consequences of membrane damage underscores the importance of maintaining the integrity of this vital structure.
Animal Cell Function of Cell Membrane in Medical Research
The animal cell function of the cell membrane has significant implications for medical research. Scientists study the membrane to understand how it contributes to health and disease. For example, research on membrane proteins has led to the development of drugs that target specific receptors, providing treatments for conditions like hypertension and diabetes. By exploring the role of the cell membrane in disease processes, researchers can develop more effective therapies.
Additionally, the cell membrane is a focus of research in areas like cancer and infectious diseases. Understanding how pathogens interact with the membrane can lead to new strategies for preventing infections. Similarly, studying how cancer cells alter their membranes to evade the immune system can provide insights into potential treatments. These advancements highlight the importance of the animal cell function of the cell membrane in advancing medical science.
Why Is the Cell Membrane Essential for Life?
The cell membrane is essential for life because it serves as the interface between the cell and its environment. Without this structure, cells would be unable to regulate the movement of substances, communicate with other cells, or maintain their internal environment. The animal cell function of the cell membrane is fundamental to all living organisms, as it enables cells to perform the processes necessary for survival.
From protecting the cell to facilitating communication and transport, the cell membrane plays a multifaceted role in cellular function. Its ability to adapt to changing conditions ensures that cells can thrive in diverse environments. By understanding the importance of the cell membrane, we can appreciate the complexity and resilience of life at the cellular level.
Understanding The Calories In A Bread: A Complete Guide
Choosing The Right Wire Gauge For 100 Amp Service: A Complete Guide
Exploring The Unique Characteristics Of Lakes And Ponds
Cell Membrane Definition And Function Functions Functions and Diagram
Top 150 + Plasma membrane in animal cell